Figure 3.
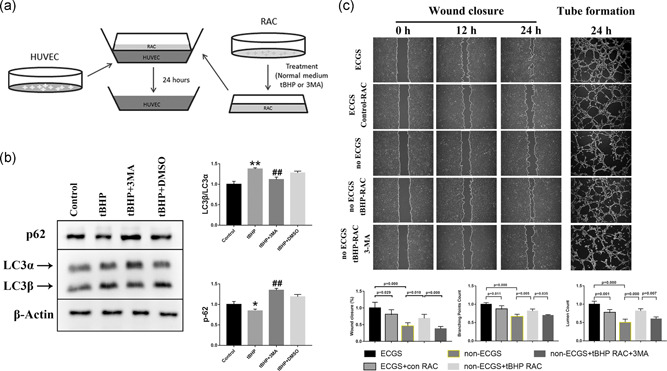
RACs have different effects on HUVEC tube formation and migration under different autophagy levels in coculture systems. (a) The diagram for establishing a coculture system for RACs and HUVECs. (b) tBHP could increase the LC3β/LC3α ratio and decrease p62 expression, while this effect was reversed by 3MA treatment. (c) The wound closure and tube formation assays of HUVECs cocultured with normal or tBHP‐treated RACs at different time points. The normal RACs could block the ECGS improvement on HUVEC function. However, the oxidative stress RACs treated with tBHP led to a significant elevation in HUVEC tube formation and migration in the no ECGS group. After inhibiting RAC autophagy by 3MA, the enhancement of tBHP RACs on HUVECs was obviously reduced. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. 3MA, 3‐methyladenine; ECGS, endothelial cell growth supplement; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cell; LC3α, light chain 3α; LC3β, light chain 3β; RAC, retinal astrocyte; tBHP, tert‐butyl hydroperoxide. *p < .05 and **p < .01 versus the control; ## p < .01 versus the tBHP group
