Figure 7.
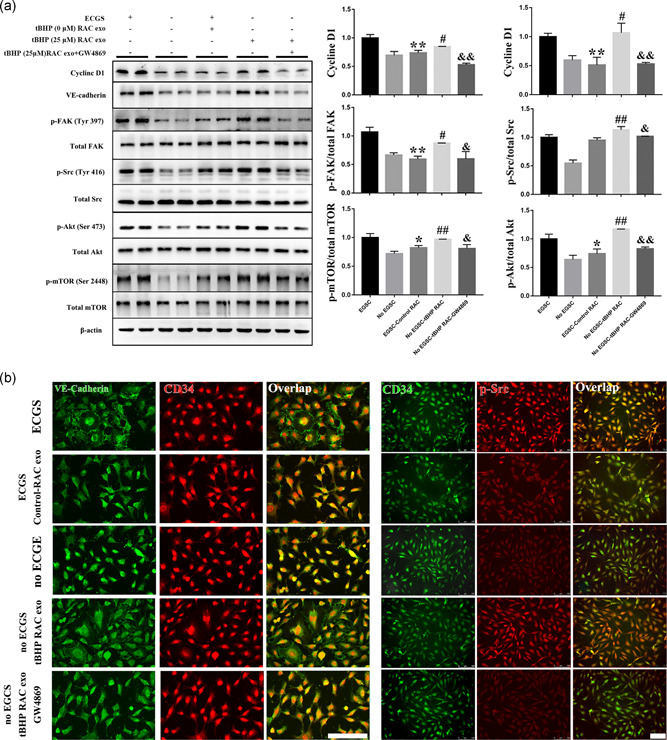
The proliferation‐ and migration‐related pathways are highly inhibited by normal RAC exosomes and are enhanced by exosomes derived from RACs with high‐autophagy levels. (a,b) The activity of the Src–FAK–Akt–mTOR pathway expression of cyclin D1 and VE‐cadherin were reduced by normal RAC‐derived exosomes when compared with the ECGS groups. However, the tBHP‐RAC exosomes can obviously elevate the pathway activity expression of cyclin D1 and VE‐cadherin compared with the no ECGS group. Moreover, GW4869 can block the tBHP‐RAC exosome effects on the related pathway in HUVECs. Scale bar = 100 μm. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. ECGS, endothelial cell growth supplement; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cell; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; RAC, retinal astrocyte; tBHP, tert‐butyl hydroperoxide; VE, vascular endothelial. *p < .05 and **p < .01 versus ECGS; # p < .05 and ## p < .01 versus no ECGS; & p < .05 and && p < .01 versus no the ECGS‐tBHP RAC group
