Figure 6.
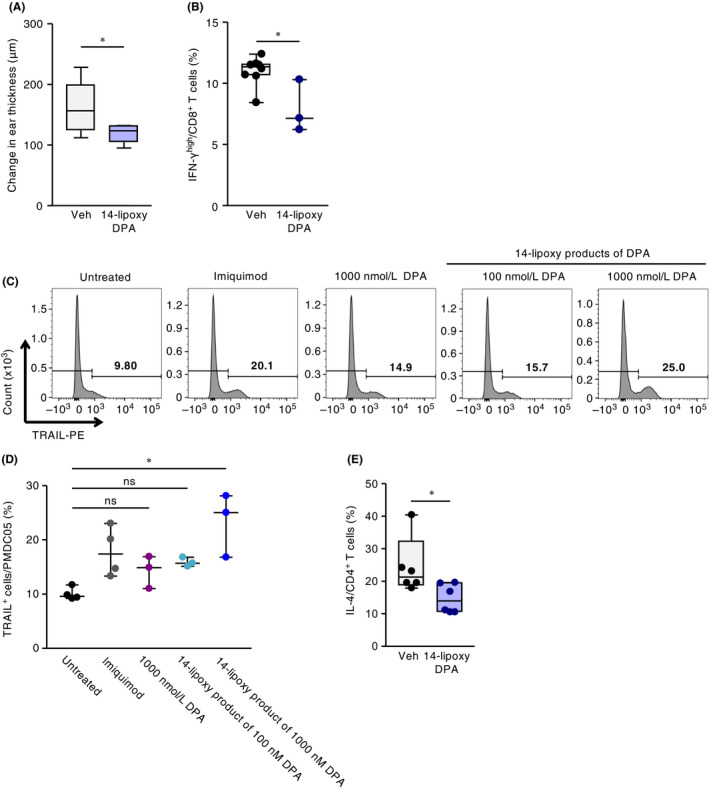
Exogenous 14‐lipoxygenation products of DPA suppressed infant CHS responses in vivo with the induction of TRAIL+ pDC and the suppression of T‐cell activation in vitro. Infant mice were intraperitoneally injected with 14‐lipoxygenation products of DPA (14‐lipoxy DPA) or vehicle (Veh) at 30 min and 1 and 3 days before DNFB sensitization and at 30 min and 1 and 3 days before DNFB challenge; (A) ear swelling was evaluated at 48 h after DNFB challenge. (B) The ratio of IFN‐γhigh–producing CD8+ T cells in infant skin at 48 h after DNFB challenge, as determined by using flow cytometry. Horizontal lines indicate median values. P values were obtained by using the Mann‐Whitney U test (*P < .05). Data were pooled for pups from three representative independent dams with reproducible results. (C, D) PMDC05 cells were treated with DPA, its 14‐lipoxygenation (14‐lipoxy) products, or imiquimod (5 μg/μL), and subsequent TRAIL expression was evaluated by using flow cytometry. (C) A representative histogram and (D) the proportion of TRAIL+ cells are shown. Horizontal lines indicate median values. P values were obtained by using Dunn's multiple‐comparison test (*P < .05). Data are pooled from two independent experiments with reproducible results. (E) PBMCs were stimulated with anti‐human CD3/CD28 antibody in the presence of PMDC05 cells with or without 1 μM of 14‐lipoxygenation product of DPA (14‐lipoxy DPA); subsequent IL‐4 expression in T cells was evaluated by using flow cytometry. Horizontal lines indicate median values. P values were obtained by using the Mann‐Whitney U test (*P < .05). Data are representative of two independent experiments with reproducible results
