Figure 3.
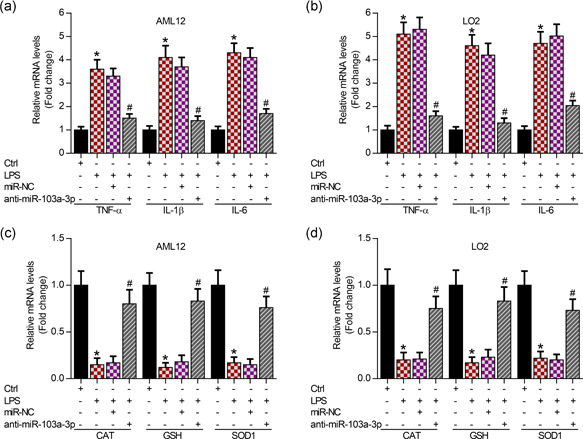
Knockdown of miR‐103a‐3p inhibits inflammation and increases antioxidation activity. (a, b) qRT‐PCR analysis showing the expression of inflammatory factors (TNF‐α, IL‐1β, and IL‐6) in AML12 and LO2 cells post 48‐hr transfection with anti‐miR‐103a‐3p followed by 24‐hr LPS incubation (50 μg/ml), *p < .01 versus Ctrl group, # p < .01 versus LPS+miR‐NC group. (c, d) qRT‐PCR analysis showing expression of antioxidation genes (CAT, GSH, and SOD1) in AML12 and LO2 cells post 48‐hr transfection with anti‐miR‐103a‐3p followed by 24‐hr LPS incubation (50 μg/ml). CAT, catalase; IL, interleukin; GSH, glutathione; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; miR, microRNA, NC, negative control; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor. *p < .01 versus Ctrl group, # p < .01 versus LPS+miR‐NC group
