Figure 2.
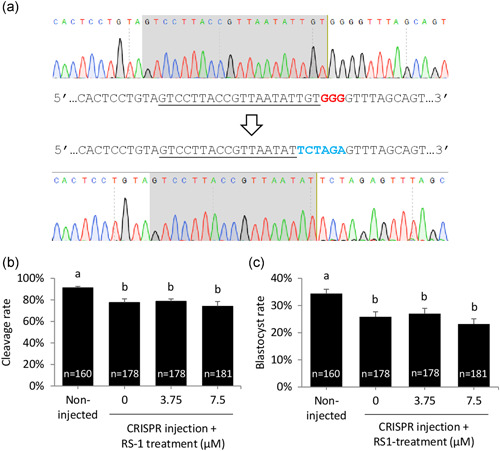
(a) HDR template design. Upper chromatogram corresponds to WT sequence, target sequence is shaded in gray in the chromatogram and underlined in the sequence, PAM (GGG) is marked by red bold letters. Lower chromatogram shows a knocked‐in allele: HDR template was designed to introduce a XbaI site (TCTAGA, marked by blue bold letters) substituting six nucleotides including PAM sequence to prevent CRISPR recognition of the edited template. (b,c) Developmental rates of CRISPR‐injected bovine embryos transiently exposed to 0, 3.75 or 7.5 µM RS‐1 compared to non‐injected control. Cleavage (b) and Day 9 blastocyst (c) rates are depicted. The number of embryos for each group is indicated inside each column. Different letters indicate significant differences based on analysis of variance. HDR, homology directed repair; WT, wild type; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif; CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. p < .05
