Figure 1.
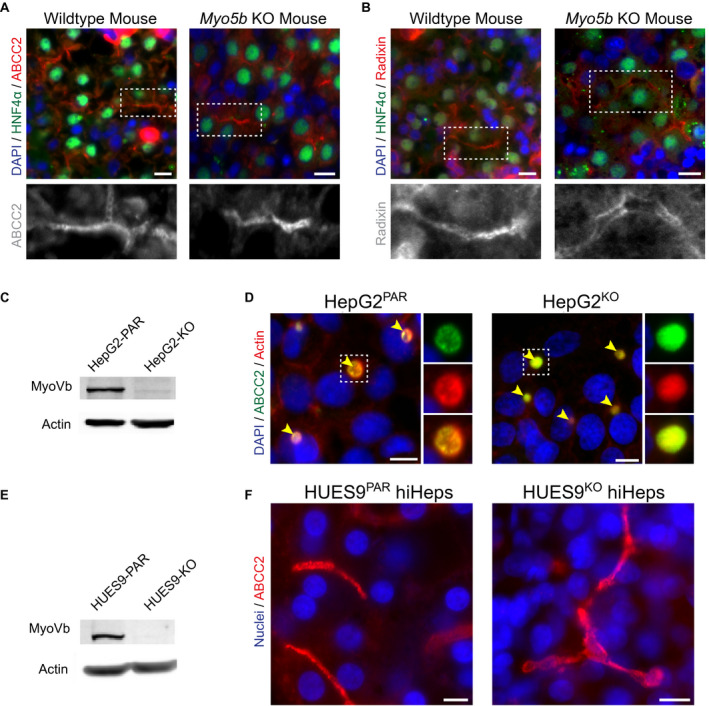
MyoVb deficiency does not disrupt canalicular protein localization. (A,B) Immunofluorescent staining of ABCC2 and radixin reveals their canalicular localization in both wild‐type and Myo5b KO mouse liver sections. HNF4α costaining marks hepatocytes. (C) KO of MYO5B in HepG2KO cells (treated with MYO5B‐targeting pLentiCRISPR V2) was confirmed by western blot (compared with parental line, HepG2PAR). (D) In HepG2 cells, localization of ABCC2 and F‐actin is unaffected by MYO5B KO (HepG2KO) compared with HepG2PAR control. Yellow arrowheads indicate BCs. (E) Western blot for myoVb in HUES9KO cells confirmed MYO5B KO (compared with parental line, HUES9Par). (F) HiHeps generated from HUES9KO cells exhibit BC formation comparable with HUES9Par‐derived hiHeps, with exclusive canalicular labeling of ABCC2. Scale bars: 10 μm.
