Figure 3.
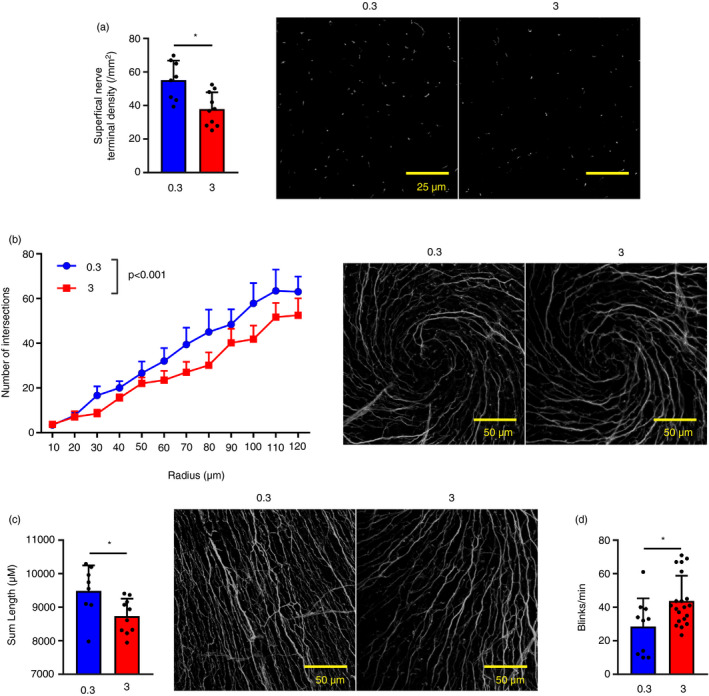
Tear hyperosmolarity (THO) affects corneal intraepithelial nerves. Mice were exposed to isoosmolar (0·3 Osm/l) or hyperosmolar (3 Osm/l) treatment for 5 days before physiological testing and death. Corneal nerves were stained with an anti‐tubulin β3 antibody. (a) Quantification of intraepithelial nerve terminals (left) and representative images (right, green: tubulin β3). (b) Quantification (Sholl analysis) of central sub‐basal nerve density (left, mean ± SEM of nerve intersections for each concentric shell of specified radius) and representative images (right, white: tubulin β3). (c) Quantification (sum length) of peripheral sub‐basal nerve density (left) and representative images (right green: tubulin β3). (d) Blinking response to a hypertonic stimulus (number of blinks over 1 min). For all experiments, pooled data (mean ± SD unless otherwise specified) from two independent experiments, n = 3–5 mice/group. *Indicates a statistically significant difference, as determined by Student’s t‐test or two‐factor anova for Sholl analysis (treatment and radius).
