Fig. 3.
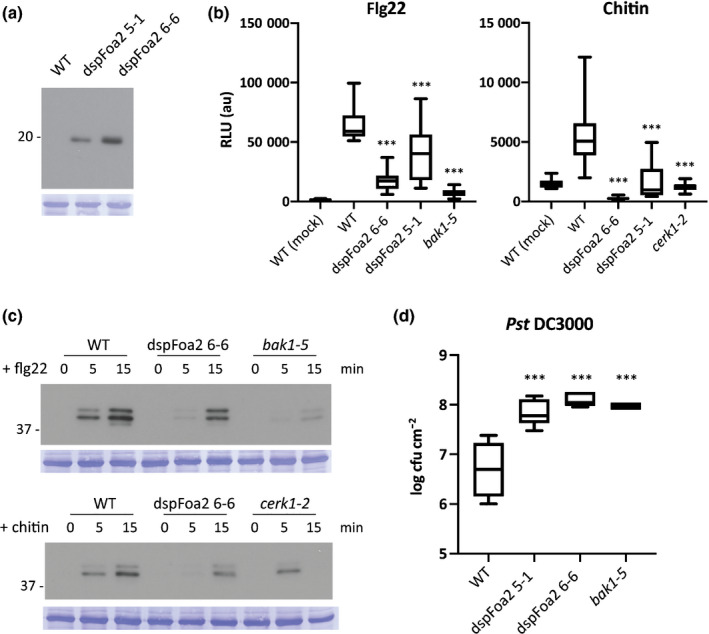
dspFoa2‐expressing Arabidopsis plants show diminished pathogen‐associated molecular pattern (PAMP) responses and enhanced pathogen susceptibility. (a) Anti‐HA Western blot revealing dspFoa2 accumulation in two independent transgenic lines. (b) Flg22‐triggered and chitin‐triggered reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in dspFoa2‐expressing Arabidopsis plants. Statistically significant differences to the flg22‐ and chitin‐treated wild‐type controls are indicated (one‐way ANOVA: ***, P < 0.001). Boxes extend from the 25th to the 75th percentile, whiskers from lowest to highest values, bar indicates the median; n = 12 leaf discs. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (c) Flg22‐triggered and chitin‐triggered activation of mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinases in dspFoa2‐expressing Arabidopsis plants. Leaf discs were treated with elicitors for 0, 5 or 15 min and the accumulation of phosphorylated MAP kinases monitored by Western blot. Molecular weight (kDa) markers are shown on the left. Equal loading is verified by Coomassie staining of the blots. WT, wild‐type. (d) Five‐wk‐old Arabidopsis plants were spray inoculated with Pst DC3000, and bacterial titres were measured at 4 d post inoculation. Statistically significant differences to the wild‐type control are indicated (one‐way ANOVA: ***, P < 0.001). Boxes extend from the 25th to the 75th percentile, whiskers from lowest to highest values, bar indicates the median; n = 5. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
