Figure 5.
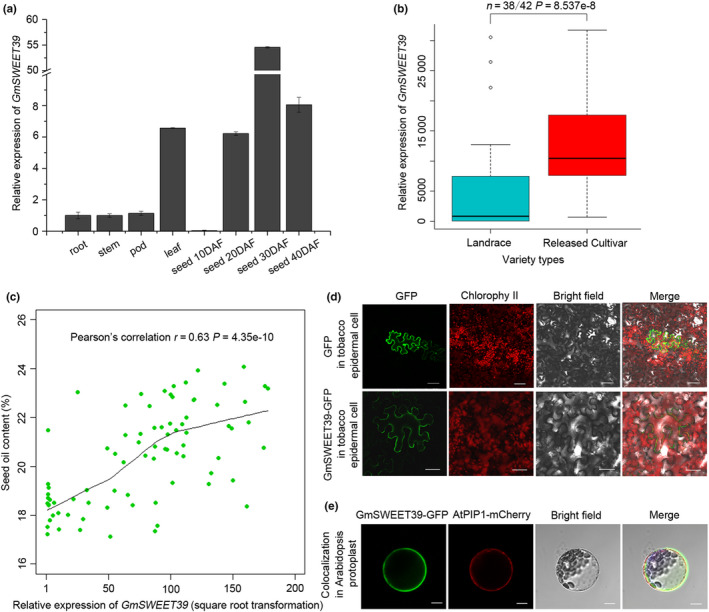
Expression patterns of GmSWEET39 and the subcellular localization of its protein. (a) GmSWEET39 expression in various tissues of soybean (Glycine max) variety Kexin4. The root, stem and leaf samples were collected from 2‐wk‐old seedlings, whereas the pods in 2‐cm length and seeds at four developmental stages were collected at 10, 20, 30 and 40 d after flowering (DAF). The level of GmSWEET39 expression was normalized to that in stems and GmUKN1 was used as the internal control. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3). (b) Boxplots of GmSWEET39 expression levels in the seeds (30 DAF) of landraces (n = 38) and released cultivars (n = 42). The levels of GmSWEET39 expression were normalized to that in Wandouzao which contains 17.21% of seed oil content. GmUKN1 was used as the internal control. The central bold line within the box represents the median; box edges indicate the upper and lower quantiles; whiskers show the 1.5 × interquartile range and points indicate outliers. P‐values were determined by two‐tailed two‐sample Wilcoxon test. (c) Correlation analysis between seed oil content and GmSWEET39 expression level in the seeds (30 DAF) of 80 soybean accessions as shown in (b). The relative expression level of GmSWEET39 was square root‐transformed. r and P values were determined by Pearson’s correlation, and the trend line was drawn using the locally weighted scatterplot smoothing (LOWESS) method. (d) Transient expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) protein or GmSWEET39‐GFP fusion protein under the control of CaMV 35S promoter in tobacco cells. Bars, 50 μm. (e) Subcellular co‐localization of transiently expressed GmSWEET39‐GFP fusion protein with a plasma membrane marker (AtPIP1) in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Bars, 10 μm. SWEET, Sugars Will Eventually be Exported Transporter.
