Figure 4.
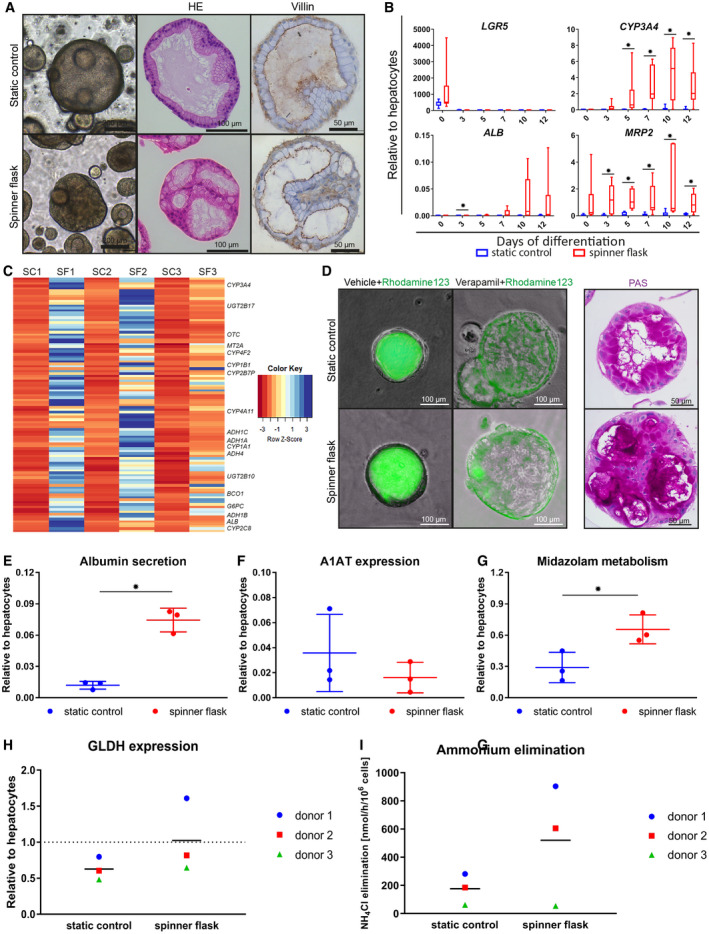
Organoid differentiation into functional hepatocytes in spinner flasks. Organoids were differentiated in spinner flasks or under static controls for 12 days. (A) Light microscopy images, HE stainings, and immunohistochemical analyses of paraffin‐embedded organoids for the canalicular marker Villin‐1. Nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin. Expression of hepatocyte markers in differentiated organoids, determined by quantitative RT‐PCR (B) and mRNA‐sequencing (C). (B) Transcript levels of LGR5, CYP3A4, ALB, and MRP2. Graphs indicate five independent experiments for five different donors. Cryopreserved hepatocytes were used as positive control. (C) mRNA sequencing on organoids from three independent donors at day 12 of differentiation. Genes that were more than 4‐fold up‐regulated in the spinner flasks at day 12 of differentiation compared with the respective static controls are shown in a heatmap. Some well‐known hepatic genes are annotated. For a full list of genes and their liver‐related functions, see Supporting Table S4. (D) Rh123 transport was determined as readout for MDR1 activity, and PAS staining indicates glycogen storage in organoid cells. (E‐I) Hepatocyte functionality of spinner flask organoids was assessed. Three independent donors were analyzed in three independent experiments. Graphs indicate mean ± SD. Cryopreserved hepatocytes cultured for 24 hours in standard sandwich culture served as a positive control. ALB concentration in supernatant (E) and intracellular A1AT levels (F). Midazolam metabolism (G) was determined as readout for CYP3A4 functionality. Intracellular GLDH levels (H) and ammonium elimination (I) from the culture medium. *P ≤ 0.05. Abbreviations: ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; BC01, beta‐carotene oxygenase 1; G6PC, glucose‐6‐phosphatase catalytic subunit; MT2A, metallothionein 2A; OTC, ornithine carbamoyltransferase; PAS, Periodic acid–Schiff; SC, static control; SF, spinner flask; UGT2B17, UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 2 member B17.
