Figure 1.
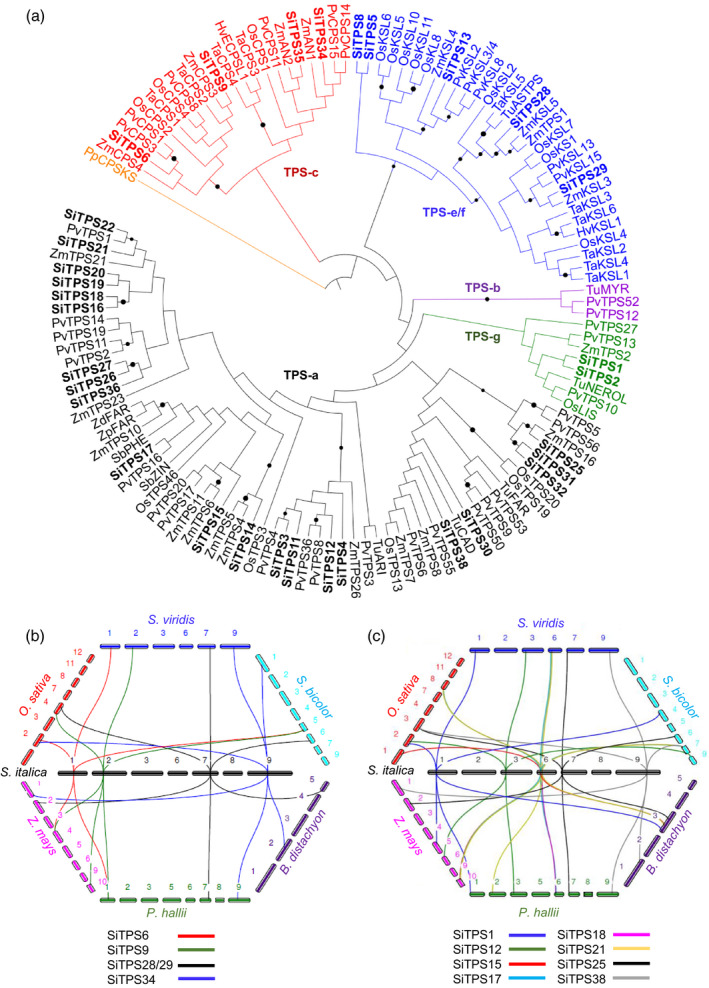
Phylogenetic and gene synteny analysis of Setaria italica terpene synthases (TPSs).
(a) Maximum likelihood phylogeny of S. italica TPSs (bold) and selected TPS‐c, TPS‐e/f, TPS‐g and TPS‐a2 clade TPSs from related poaceous crop species. Tree rooted with the ent‐CPP/ent‐kaurene synthase from Physcomitrella patens, PpCPS/KS. Black circles denote bootstrap support of > 80% (1000 repetitions). Accession numbers and protein sequences are given in Table S1.
(b), (c) Synteny and orthology of diterpene synthases (b) and sesquiterpene synthases (c) between S. italica, Setaria viridis and related diploid poaceous grasses. All chromosomes for Zea mays (magenta), Panicum hallii (green), Brachypodium distachyon (purple), Sorghum bicolor (cyan), S. viridis (blue) and Oryza sativa (red) are arranged in a polygon to emphasize synteny with S. italica (black). Chromosome IDs are given on each line segment. A syntenic network is depicted as a colored line specific to a TPS gene located on S. italica chromosomes (black) connecting to respective syntenic orthologs on chromosomes of other genomes (Table S3).
