Figure 4.
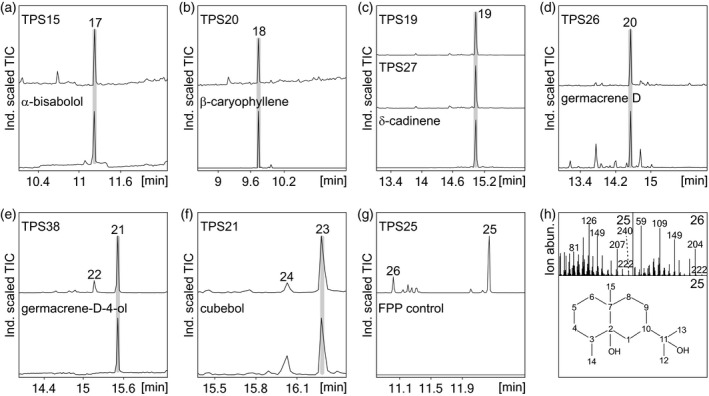
Functional characterization of the Setaria italica class I sesquiterpene synthases.
(a)–(e) The GC‐MS traces of reaction products resulting from Nicotiana benthamiana co‐expression assays of the focal S. italica sesquiterpene synthases with product identification by comparison with authentic standards identified SiTPS15 as an α‐bisabolol synthase (a), SiTPS20 as a β‐caryophyllene synthase (b), SiTPS19 and SiTPS27 as δ‐cadinene synthases (c), SiTPS26 as a germacrene d‐synthase (d) and SiTPS38 as a germacrene‐d‐4‐ol synthase (e). (f), (g) The GC‐MS traces of reaction products resulting from Escherichia coli co‐expression assays of the maize E,E‐farnesyl pyrophosphate (E,E‐FPP) synthase, ZmFPPS (Cervantes‐Cervantes et al., 2006), with focal S. italica sesquiterpene synthases identified SiTPS21 as a cubebol synthase (f), whereas SiTPS25 produced two distinct products, compound 25 and a minor byproduct, compound 26 (g). (h) Mass spectrum of compounds 25 and 26, and NMR‐verified structure of compound 25 identifying the SiTPS25 product as eudesme‐2,11‐diol. Mass spectra for all detected compounds are given in Figure S3. 17, α‐bisabolol; 18, β‐caryophyllene; 19, δ‐cadinene; 20, germacrene D; 21, germacrene‐D‐4‐ol; 22, unidentified terpene product; 23, cubebol; 24, unidentified terpene product; 25, eudesme‐2,11‐diol; 26, unidentified terpene product.
