Figure 6.
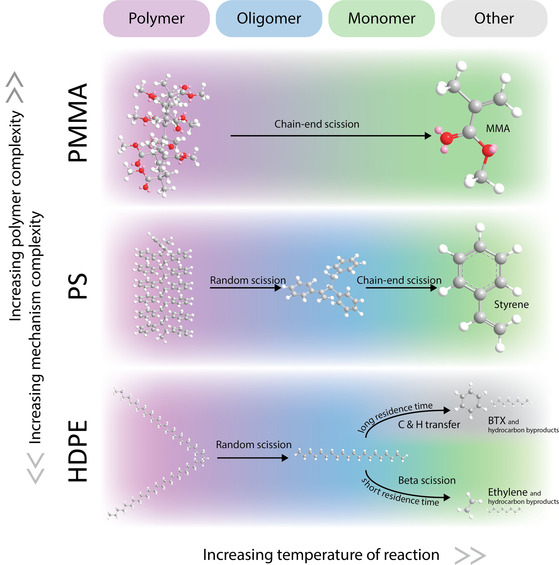
With an increase in the number of functional groups and heteroatoms in the backbone of the polymer (top), the distribution of products and the pyrolytic mechanisms become less complicated. Process parameters provide a higher degree of control over the product distribution for polyolefins, in this example HDPE, although the ultimate monomer yield is lower than for PS and PMMA. A common theme of all pyrolysis is that an excessively high temperature leads to coke formation given that the residence time is long enough. Although, most reaction steps occur at lower temperatures, similar trends are observed for catalytic processes. BTX denotes benzene, toluene, and xylene.
