Fig. 1.
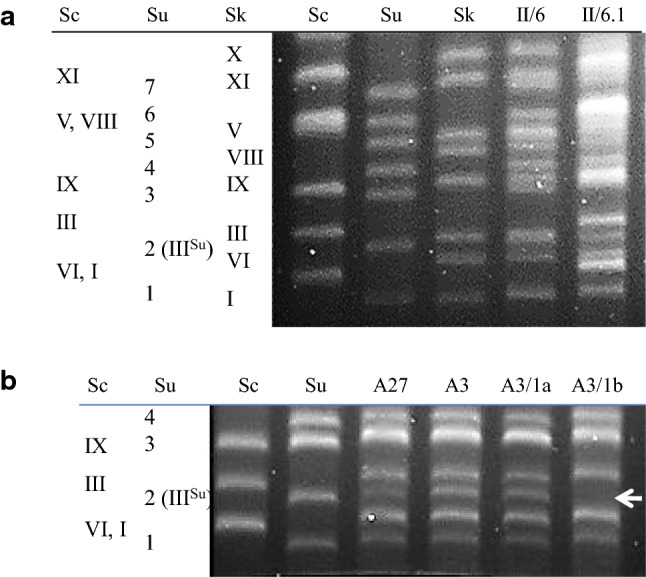
Karyotypes of parental strains, hybrids and spore clones. a Karyotypes of a two-species kudvarum hybrid, a three-species cekudvarum hybrid and the parental strains. Only the regions of smaller chromosomes are shown in which individual bands can be distinguished in the cekudvarum karyotype. b Karyotypes of two-species cevarum hybrids and spore clones. Only the regions containing the bands of the MAT-carrying chromosomes are shown. The columns on the left sides of the gel photographs show the conventional numbering of chromosomes in the S. cerevisiae, S. uvarum and S. kudriavzevii genomes. The S. uvarum chromosomes are numbered according to Nguyen et al (2000). Sc: S. cerevisiae 10-170; Sk: S. kudriavzevii 10-1653; Su: S. uvarum 10-522; II/6: kudvarum hybrid; II/6.1: cekudvarum hybrid; A27 and A3: cevarum hybrids, A3/1a: sterile spore clone of A3; A3/1b: fertile spore clone of A3. Arrowhead marks the position of the missing Chr IIISu (Chr 2) in the fertile spore clone A3/1b
