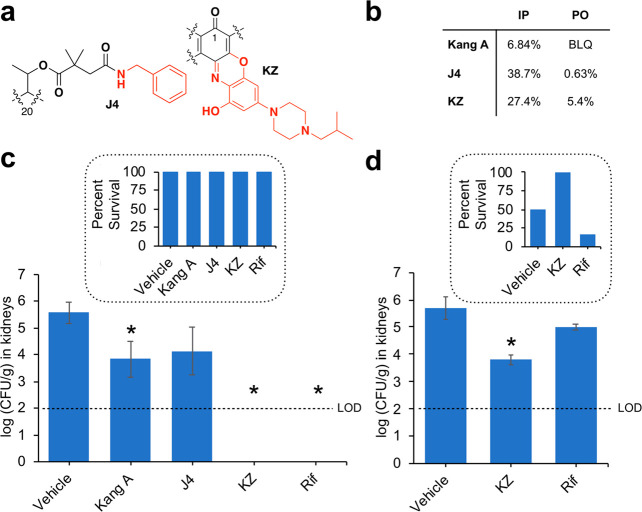
Figure 5.
In vivo activity of top leads from semisynthesis in comparison to Kang A and Rif. (a) Structural modifications of lead compounds: the J4 Kang amide and the KZ benzoxazino analogue. (b) IP and PO bioavailability of J4 and KZ in comparison to Kang A. BLQ, below limit of quantification. (c) Efficacy of Kang A, J4, KZ, and Rif in treating MRSA in a neutropenic murine acute peritonitis/septicemia model. (d) Efficacy of KZ and Rif in treating infection with a highly virulent S. aureus strain with RifR S486L RNAP in the neutropenic murine acute peritonitis/septicemia model. For panels (c) and (d), infected mice received IP injections of drug (15 mg/kg) or vehicle (5% DMA plus 30% Captisol) at 2, 4, and 8 h post infection. The y-axis indicates bacterial burdens in kidneys at 24 h postinfection. Limit of detection (LOD) for burden quantification was calculated as 100 CFU/g of kidney. The results shown represent the average bacterial burden from six mice. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Asterisks indicate treatments that resulted in a statistically significant reduction in burden (P < 0.05) relative to the vehicle treated group. Insets, percent survival of mice at 24 h for each treatment.