Figure 1.
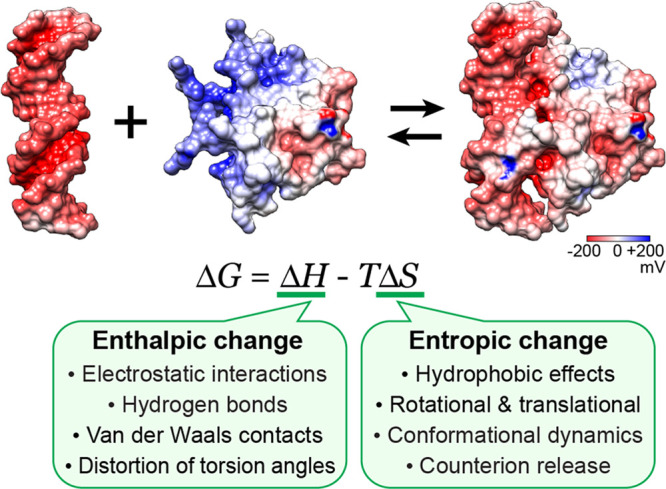
Key factors that influence the enthalpic (ΔH) and entropic (ΔS) terms of the binding free energy ΔG for formation of a protein–nucleic acid complex. The main factors of the entropic changes are (1) the hydrophobic effects that accompany a decrease in nonpolar surface areas exposed to the solvent, (2) rotational and translational restrictions of the interacting macromolecules, (3) conformational dynamics, and (4) counterion release. Empirical formulas for these entropic effects are given in ref (9). The structures of the MEF2A DNA-binding domain, a DNA duplex, and their complex (PDB 1EGW) are shown with surface electrostatic potentials.
