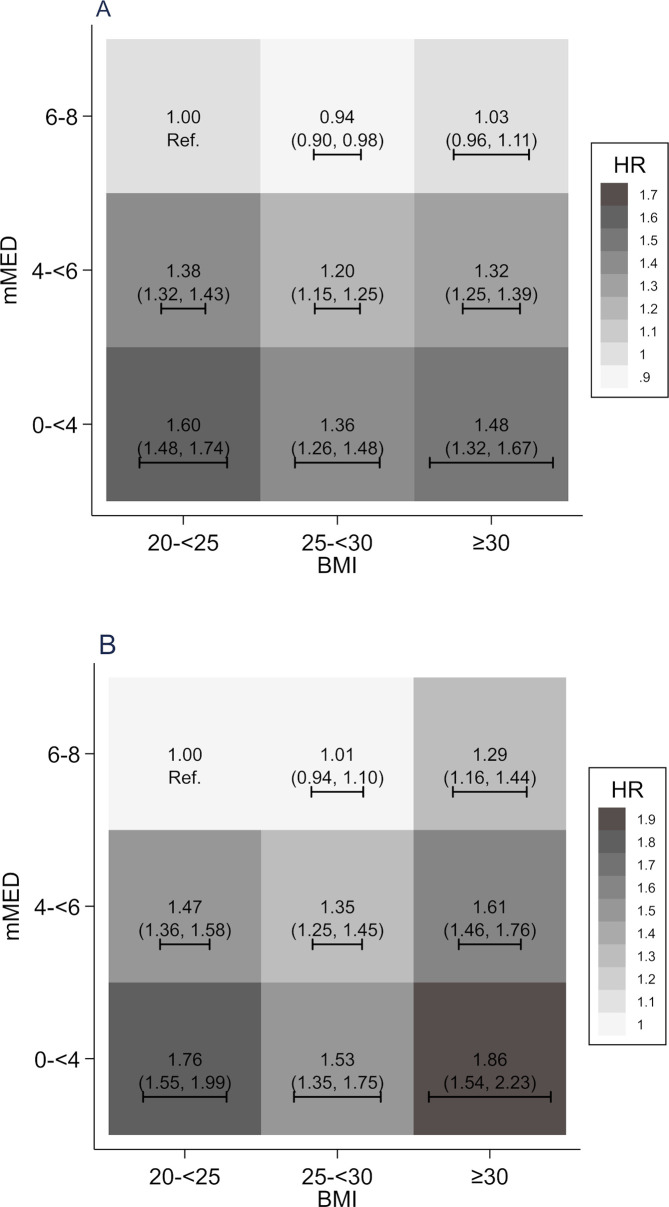
Fig 3. Associations of combinations of BMI and adherence to an mMED with all-cause (A) and CVD mortality (B).
Estimated by multivariable-adjusted HRs by use of Cox regression analysis with a normal BMI and high adherence to mMED as the reference. The CI in each subpanel is expressed both in numbers and as a line representing the width. HRs adjusted for sex, age (splines with 2 knots), educational level (≤9, 10–12, >12 years, other), living alone (yes or no), leisure time physical exercise during the past year (<1 h/w, 1 h/w, 2–3 h/w, 4–5 h/w, >5 h/w), walking/cycling (almost never, <20 min/d, 20–40 min/d, 40–60 min/d, 1–1.5 h/d, >1.5 h/d), height (splines with 2 knots), energy intake (splines with 2 knots), smoking habits (current, former, never), Charlson’s weighted comorbidity index (continuous; 1–16), and diabetes mellitus (yes/no). BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HR, hazard ratio; mMED, modified Mediterranean-like diet.