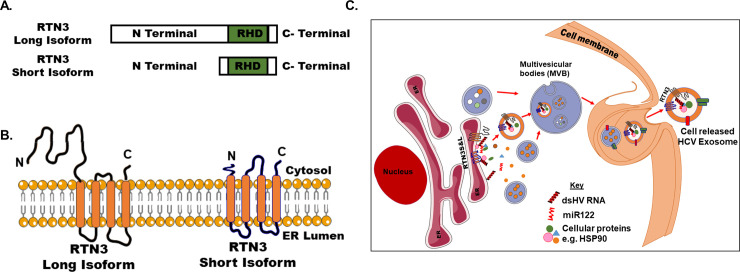
Fig 6. Schematics of RTN3 facilitates the loading of infectious HCV exosomes.
(A) Schematic illustration of RTN3 long and short isoforms (RTN3&S) and (B) their cellular endoplasmic reticulum (ER) locations. (C) HCV infection is associated with increased expression of double-stranded (ds) HCV RNA in Huh7 cells. Double-stranded HCV RNA can interact with endoplasmic reticulum located RTN3L&S protein isoforms HCV infected Huh7 cells. Additionally, direct or indirect interactions also occur between other cellular proteins and nucleic acids with dsHCV RNA and RTN3L&S in HCV infectedHuh7 cells. RTN3L&S in HCV infected Huh7 cells can directly modulate the incorporation of replication-competent HCV dsRNA in association with other proteins inside membrane vesicles which are translocated to multivesicular bodies (MVB). This MVB in HCV infected Huh7 cells then fuse with the plasma membrane resulting in the release of infectious viral exosomes. Schematic illustration made use of some smart servier medical art templates (https://smart.servier.com).