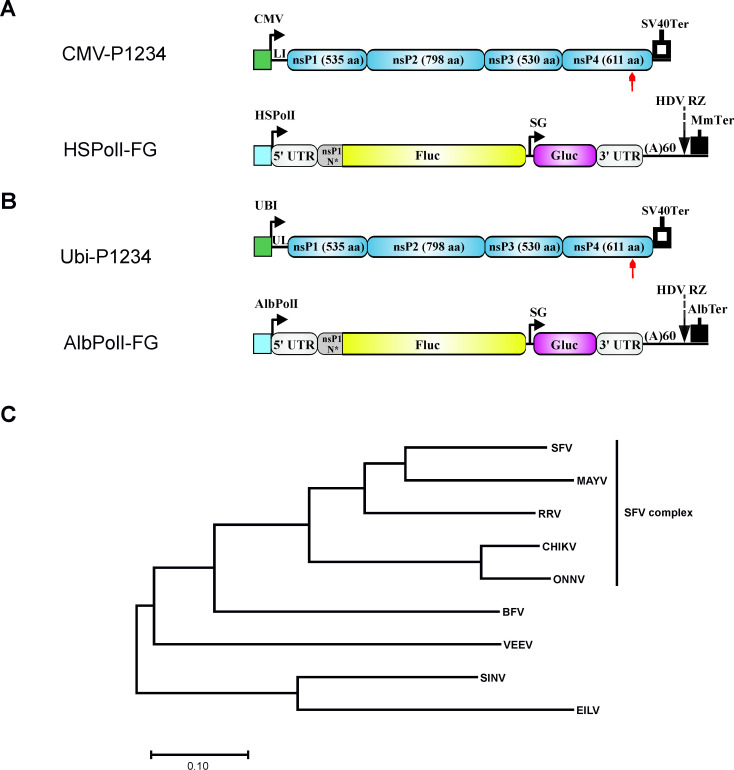
Fig 1. Alphaviruses selected for the analysis and designs of trans-replication tools.
(A) Schematic representation of constructs for human cells. CMV, immediate early promoter of human cytomegalovirus; LI, leader sequence of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene with artificial intron; SV40Ter, simian virus 40 late polyadenylation region; HSPolI, a truncated promoter (residues −211 to −1) for human RNA polymerase I; MmTer, a terminator for RNA polymerase I in mice. (B). Schematic representation of constructs for Aedes albopictus cells. UBI, polyubiquitin promoter of Aedes aegypti; UL, leader sequence of Aedes aegypti polyubiquitin gene with a natural intron; AlbPolI–truncated promoter (residues −250 to −1) for Aedes albopictus RNA polymerase I; AlbTer–putative terminator for Aedes albopictus RNA polymerase I. (A, B) 5′ UTR, full length 5’ UTR of an alphavirus; 3’ UTR, truncated (last 110 residues) 3′ UTR of an alphavirus; SG—SG promoter spanning (with respect to termination codon of nsP4) from position -79 to the end of intergenic region, nsP1 N*—region encoding the N-terminal 77 to 114 amino acid residues of nsP1, depending on the virus; HDV RZ—antisense strand ribozyme of hepatitis delta virus. Red arrow indicates the location of the GDD motif in nsP4; in polymerase negative constructs this was replaced by GAA. The vector backbones are not shown and drawings are not to scale. (C) Phylogenetic tree of replicases of analysed alphaviruses. Phylogenetic tree was constructed using evolutionary analysis by Maximum Likelihood method and JTT matrix based model. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitution per site. This analysis involved sequences of P1234 of indicated viruses. Evolutionary analysis was conducted using MEGA-X software.