Figure 1.
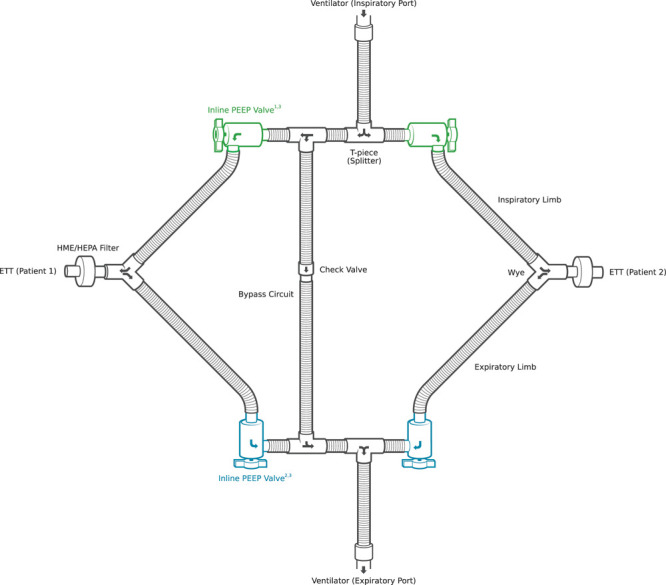
Differential multiventilation (DMV). An example of a simplified DMV circuit with the four inline positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) valves highlighted. The most fundamental component for these improved multiventilation systems is the inline PEEP valve. In DMV setups, inline PEEP valves serve the following three key functions: 1) reduce delivered inspiratory pressure to an individual patient circuit, 2) increase end-expiratory pressure for an individual patient circuit, and 3) act as an one-way valve to ensure unidirectional gas flow through the divided circuit. While the monitoring components have been omitted for visual clarity in the figure, DMV systems should use individual sensors and monitoring equipment whenever possible to ensure patients are receiving adequate oxygenation and ventilation. Appropriate monitoring options include pressure manometry, flow sensors, end-tidal Co2 monitors, and noninvasive cardiac output monitors (6). ETT = endotracheal tube, HEPA = high-efficiency particulate air filter, HME = heat and moisture exchanger.
