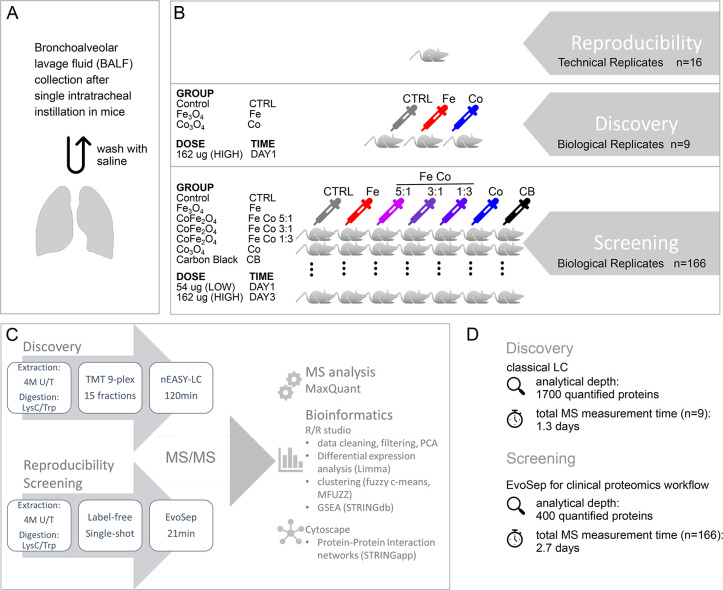
Figure 1.
Experimental design and proteome analysis workflow. (A) Mice were treated by single intratracheal instillation with either 0 μg (vehicle control, CTRL), 54 μg (low dose, LOW), or 162 μg (high dose, HIGH) of nanoparticles per animal. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was obtained by two washes with saline 1 day or 3 days postinstillation. (B) Reproducibility: To evaluate reproducibility of the Evosep One LC system technical replicates (n = 16) of a single BALF sample were measured as 21 min gradients. Discovery: In-depth BALF proteome profiling was performed on selected samples from day 1 postinstillation with high dose nanoparticle treatment (162 μg/animal). Samples of iron oxide (Fe3O4) and cobalt oxide (Co2O3) nanoparticle treatment were compared to controls with three biological replicates per group. Screening: Within the whole study the effects of six different types of nanoparticles (Fe3O4, CoFe2O4 (Fe Co 5:1), CoFe2O4 (Fe Co 3:1), CoFe2O4 (Fe Co 1:3), Co3O4, and carbon black) were tested at two doses (LOW, HIGH; except for carbon black (HIGH only)) and two time points (1 day and 3 days postinstillation). In total, BALF samples of 166 animals were measured. (C) Schematic of proteome analysis workflow. To obtain maximal proteome coverage, BALF samples of the discovery phase were prefractionated (high pH reverse phase, 15 fractions) and run as 120 min gradients with classic nanoLC system setup. Samples were TMT labeled and run together as 9plex. BALF samples of the whole study (n = 166, Screening) as well as technical replicates (Reproducibility) were run label-free as single-shot injections on 21 min gradients using the Evosep One LC system. MS raw files were analyzed by MaxQuant. Downstream bioinformatic analyses were performed within the R environment as indicated with protein–protein interaction network visualization in Cytoscape. (D) Summary of analytical depth and measurement time for Discovery and Screening phase.