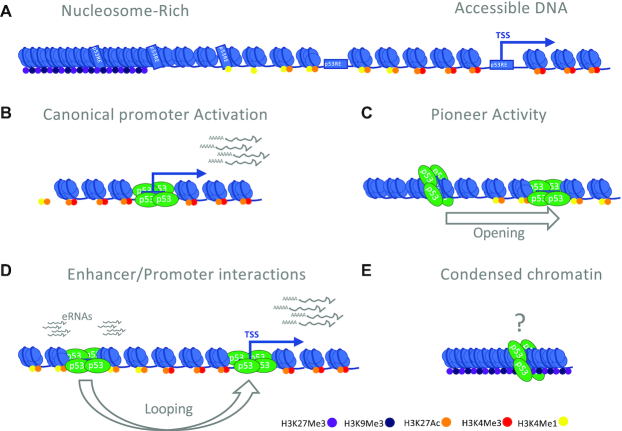
Figure 3.
Chromatin binding states of p53. (A) A general schematic of the range of chromatin states with observed p53 binding. (B) Binding of p53 to gene proximal promoters represents the canonical model for p53 engagement with gene regulatory elements. p53-bound promoters are generally characterized by accessible (nucleosome-free) chromatin and histone modification-based hallmarks such as H3K4 trimethylation (H3K4me3). (C) p53 can bind to DNA in the context of a nucleosome using pioneer factor-like activity. Pioneer factor activity reflects two related functions: the recognition of a TF motif in nucleosomal DNA and the facilitation of nucleosome remodeling to create an accessible DNA element. p53 recognizes its RE across multiple nucleosomal contexts, although binding is strongly disfavored when the p53RE is at the nucleosome dyad. The majority of nucleosome binding sites remain nucleosome-enriched (closed), although this may be context or treatment-specific. p53 binding to closed chromatin in fibroblasts, for example, leads to a subset of regions that become accessible and correlate with transcriptional enhancer activity. (D) p53 also binds to genomic regions with hallmarks of transcriptional enhancers, which includes accessible DNA, the presence of H3K4me1 and H3K27ac, and the absence of H3K4me3. p53 binding to these regions elicits transcription of bidirectional enhancer RNA (eRNA). Although very limited data currently exists regarding p53, one mechanism for distal gene regulatory element activity is through chromatin looping, which brings these elements in physical proximity to target gene promoters. (E) The final class of binding events is to condensed/closed chromatin, which can either be characterized as actively repressed heterochromatin (containing the histone modifications H3K9me3 or H3K27me3) or quiescent. Quiescent chromatin is condensed but does not have the stereotypical histone modifications associated with heterochromatin. Quiescent chromatin represents the largest individual chromatin state bound by p53, although their function is unknown (Figure 2A).