Table 1.
Components of a summary measure of cropland connectivity risk index that were evaluated in uncertainty quantification
| Method | Parameter | Levels | Interpretation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total mean |

C5mingridi is the cropland proportion of the ith 5 minute grid within a 2 degree grid |
C5mingridi | The sum of cropland proportion of all 5 × 5 minute grids within a 2° × 2° grid is divided by the total number of 5 × 5 minute grids aggregated in a 2° × 2° grid | |
| Land mean |
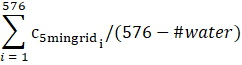
C5mingridi is the cropland proportion of the ith 5 minute grid within a 2 degree grid #water denotes the total number of 5 minute grids with water rather than agricultural land |
C5mingridi | The sum of cropland proportion of all 5 × 5 minute grids within a 2° × 2° grid is divided by the total number of 5 × 5 minute grids containing only land (5 × 5 minute grids with water are excluded) aggregated in a 2° × 2° grid | |
| Dispersal risk model (DRM) DR = cicjdij–β | Inverse power law model dij–β dij is the distance between nodes i and j ci is the fraction harvested area with the crop of interest at the ith node | β | β1 = 0.5 β2 = 1.0 β3 = 1.5 | Potential changes in model to describe different types of pests and dispersal mechanisms |
| DR = cicjexp(–γdij) | Negative exponential model exp(–γdij) dij is the distance between nodes i and j ci is the fraction harvested area with the crop of interest at the ith node | γ | γ1 = 0.05 γ2 = 0.1 γ3 = 0.2 γ4 = 0.3 γ5 = 1.0 | Potential changes in model to describe different types of pests and dispersal mechanisms |
| Cropland proportion | Minimum cropland proportion for inclusion of node in analysis | pc | pc 1 > 0.0015 pc2 > 0.002 pc3 > 0.0025 | Lower thresholds result in more nodes retained in the network |
| Link weight | Minimum link weight for inclusion of link in network | pl | pl 1 > 0.001 pl2 > 0.0001 pl3 > 0.00001 | Lower thresholds result in more links retained in the network |
Note: Each combination of the levels of the values indicated was evaluated. The combinations included varying the form of the mean (total mean or land mean) and varying the dispersal model (inverse power law or negative exponential), as well as the parameters of the model selected.
