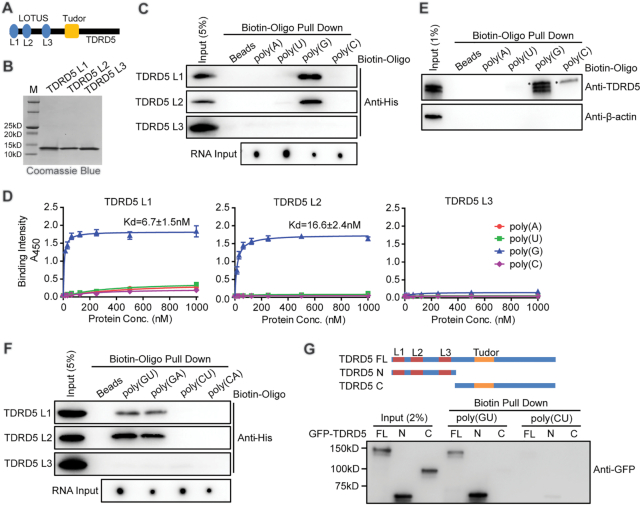
Figure 2.
TDRD5 LOTUS domains bind to G-rich RNA. (A) Domain architecture of mammalian TDRD5. Three LOTUS domains are abbreviated as L1, L2 and L3, respectively. (B) Purification of mouse TDRD5 LOTUS domains. His-tagged LOTUS domains were purified by affinity chromatography followed by gel filtration chromatography. (C) LOTUS domains specifically bind to poly(G) RNA. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotides were bound to streptavidin beads. After incubating with purified His-tagged LOTUS domains, Western blotting using an anti-His antibody was performed to detect bound LOTUS domains. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotide inputs were measured by dot blot analysis. (D) LOTUS domains specifically bind to poly(G) RNA by ELISA assays. n = 3, error bars represent s.e.m. Dissociation constants (Kd) are indicated. (E) poly(G) RNA binds endogenous TDRD5 from mouse testes. Biotin-labeled poly(G) RNA oligonucleotides were bound to streptavidin beads. After incubating with adult mouse testis lysates, Western blotting was performed using TDRD5 and β-actin antibodies. TDRD5 isoform1 and isoform2 were shown. Asterisk shows a non-specific band. (F) LOTUS domains bind to G-rich RNA. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotides were bound to streptavidin beads. After incubating with purified His-tagged LOTUS domains, Western blotting using an anti-His antibody was performed to detect bound LOTUS domains. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotide inputs were measured by dot blot analysis. (G) LOTUS domains but not the Tudor domain of TDRD5 bind to G-rich RNA. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids coding for GFP-tagged full-length (FL) or truncated (N or C) TDRD5. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotides were bound to streptavidin beads. After incubating with HEK293T cell lysates, Western blotting was performed using an anti-GFP antibody.