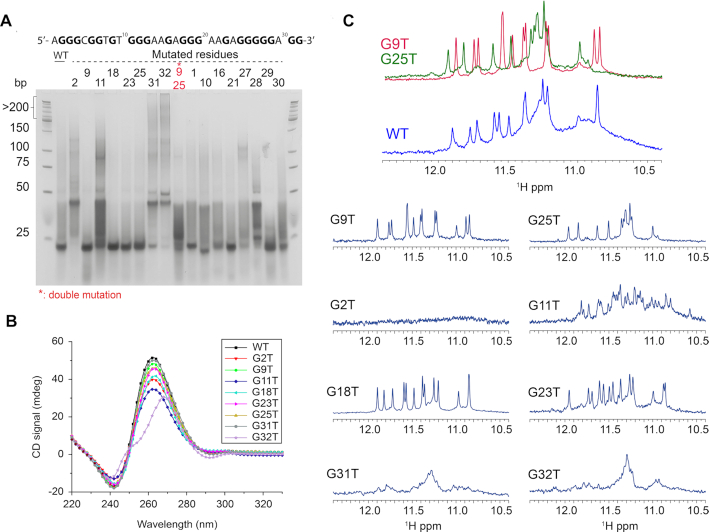
Figure 2.
(A) Native gel experiment of KRAS 32R and several simple mutants and one double mutant showing that some mutants harbor the same conformation as wild type whereas several mutants such as G2T or G32T severely impact G4 formation; (B) the CD spectra of KRAS 32R mutants at 37°C show that most of the mutations do not affect G4 conformation, showing all parallel conformation with characteristic peaks around 260 nm (positive) and 240 nm (negative), except for G32T showing signal similar to hybrid-type G4; (C) KRAS 32R mutants imino region at 37°C showing different effects of mutations in agreement with results obtained in native gel demonstrating the existence of two major conformations and the role of the 3′end residues. Imino region comparison between KRAS 32R wild type (blue), G9T and G25T showing that profiles from G9T and G25T can be found in wild type spectra as an evidence of the model. All experiments were performed in buffer 1× (50 mM KCl; 10 mM KPi; pH 6.66).