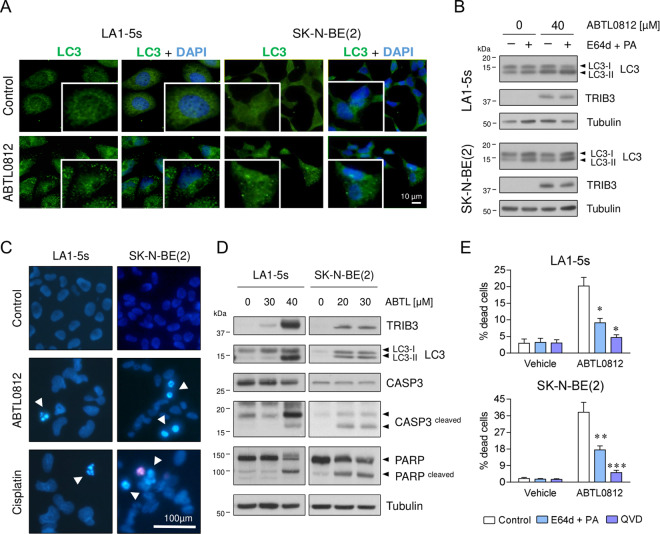
Fig. 2. ABTL0812 induces autophagy and apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells.
a Immunostaining of ABTL0812-induced autophagosome formation. Neuroblastoma cells were treated with 20 µM (SK-N-BE(2)) or 40 µM (LA1-5s) ABTL0812 for 12 h and then fixed and stained with anti-LC3 (green) and DAPI (blue). Punctuated patterns shows LC3-II recruited to the autophagosomes. b Western blot analysis of ABTL0812-induced autophagic flux. Cells were pre-treated 2 h with vehicle or 10 µM E64d and 10 µg/ml pepstatin A (PA). Then, 40 µM (LA1-5s) or 30 µM (SK-N-BE(2)) ABTL0812 was added for 6 h in the presence or absence of lysosomal inhibitors. Anti-TRIB3 was used as a control for ABTL0812 response. c Representative images of nuclear morphology assessment at 48 h post-treatment with ABTL0812 (30 µM for LA1-5s, 20 µM for SK-N-BE(2)) or vehicle. Arrowheads point towards condensed or fragmented nuclei. Cisplatin (25 µM) was used as an apoptosis positive control. d Western blot analysis of ABTL0812-induced apoptosis 72 h post-treatment. e Autophagy and apoptosis inhibitors reduce ABTL0812-induced cell death. LA1-5s and SK-N-BE(2) cells were pre-treated 2 h with vehicle (ethanol) or 10 μM E64d and 10 μg/ml PA or 20 μM QVD. 30 μM ABTL0812 for LA1-5s or 20 μM for SK-N-BE(2) were added in the presence or absence of autophagy and apoptosis inhibitors. Cell death was quantified 48 h post-treatment by scoring four representative fields of each condition (n = 3). Data is presented as the average of three independent experiments ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 compared to ABTL0812 in the absence of inhibitors.