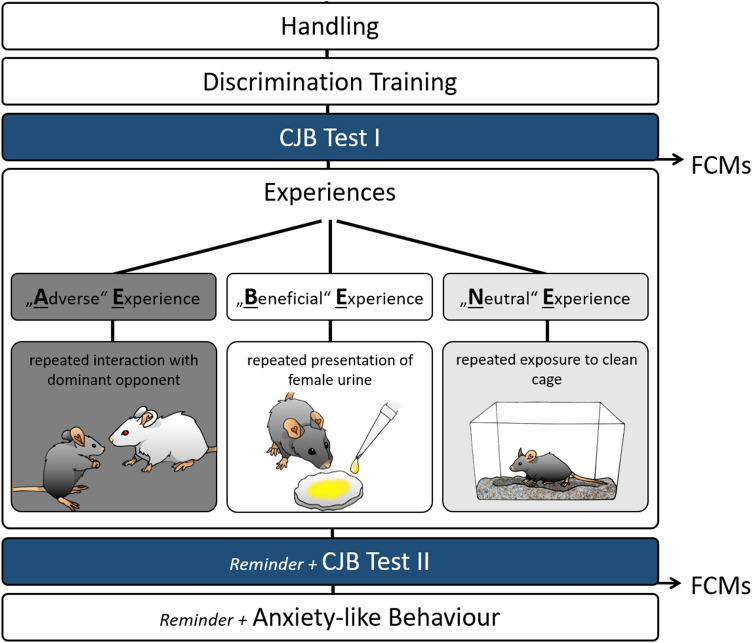
Figure 1.
Experimental design. Mice were habituated to cup handling before they underwent daily training sessions until successful acquisition of the discrimination task. Afterwards, they were tested in the cognitive judgement bias (CJB) test. During the following phase, mice repeatedly made one out of three different experiences: mildly “adverse”, “beneficial”, or “neutral”. They were then tested for their CJB again. During this second test phase, a so-called reminder was presented before each test session with the aim to re-evoke the affective state the animals experienced during the treatment phase. On the last day of each CJB test phase, faecal corticosterone metabolite concentrations (FCMs) were assessed. Subsequently, animals were tested for anxiety-like behaviour. Again, they were presented with reminders before each behavioural test.