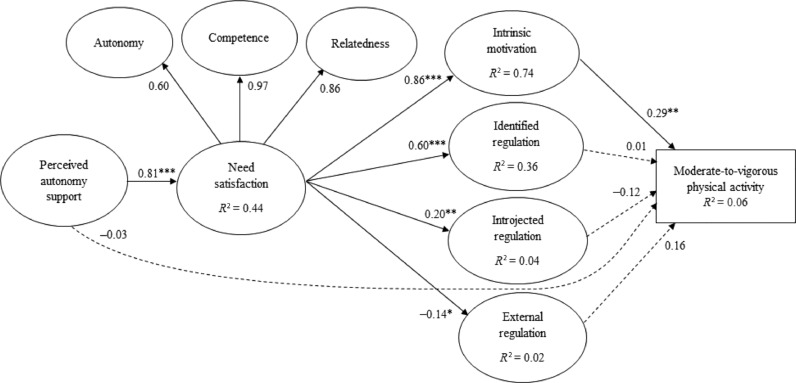
Fig. 2.
The structural equation model measuring the relationships between perceived autonomy support and MVPA through need satisfaction and motivation. Four specific indirect effects of perceived autonomy support on MVPA were tested: (1) need satisfaction and intrinsic motivation, (2) need satisfaction and identified regulation, (3) need satisfaction and introjected regulation, and (4) need satisfaction and external regulation. In addition, 4 indirect effects of perceived autonomy on motivational regulations through need satisfaction were tested. Solid lines indicate significant relationships, and dotted lines indicate nonsignificant relationships. For visual simplicity, covariances between all forms of motivations are not shown. Covariances of the disturbance terms were: rintrinsic motivation-identified regulation = 0.17, rintrinsic motivation-introjected regulation = 0.00, rintrinsic motivation-external regulation = ‐0.25**, ridentified regulation-introjected regulation = 0.50***, ridentified regulation-external regulation = 0.05, rintrojected regulation-external regulation = 0.54***. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.