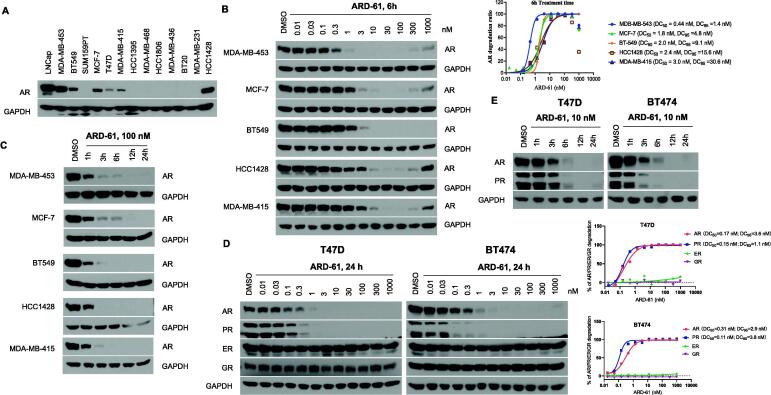
Fig. 1.
ARD-61 potently induces AR degradation in breast cancer cells. (A) Western blotting of AR expression in different breast cancer cell lines. (B) AR+ breast cancer cells were treated with different concentrations of ARD-61 for 6 h and AR protein levels were assessed by Western blot. Protein levels were quantified using ImageJ and AR degradation percentage is plotted using Prism 8.0 and GAPDH was used as the loading control. One representative AR degradation dose–response curve for each cell line is shown. (C) AR+ breast cancer cells were treated with 100 nM of ARD-61 for indicated time points and whole protein lysates were used to determine AR protein levels by Western blot. (D) T47D and BT474 cells were treated by indicated concentrations of ARD-61 for 24 h. AR, PR, GR and ER protein levels were detected by Western blotting and quantified using ImageJ. Relative AR, PR, GR and ER levels in relation to the GAPDH protein level in percentage are plotted against drug concentrations. One representative dose–response curve is shown for each cell line. (E) T47D and BT474 breast cancer cells were treated with 10 nM of ARD-61 for indicated time points. AR and PR protein levels were determined by Western blotting.