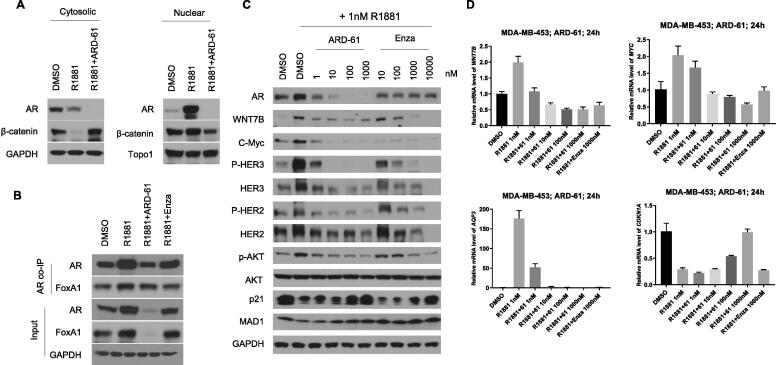
Fig. 6.
ARD-61 blocks AR signaling and represses AR-target genes expression in MDA-MB-453 cells. (A) MDA-MB-453 cells were pretreated with charcoal-stripped serum (CSS) contained medium for 72 h, and cells were then treated with 1 nM AR agonist R1881 alone or in combination with 1 µM ARD-61 for 24 h. Cytosolic and nuclear proteins were extracted and AR and β-catenin proteins were detected by Western blotting. GAPDH and Topo1 were used as the loading control for cytosolic and nuclear protein, respectively. (B) MDA-MB-453 cells were pretreated with charcoal-stripped serum (CSS) contained medium for 72 h, and cells were then treated with 1 nM AR agonist R1881 alone or in combination with 1 µM ARD-61 or 1 µM Enzalutamide (Enza) for 24 hr. Whole protein lysates were used for co-IP assay. (C) MDA-MB-453 cells were pretreated with charcoal-stripped serum (CSS) contained medium for 72 h. Cells were then treated with 1 nM AR agonist R1881 alone or in combination with different concentrations of ARD-61 or Enzalutamide (Enza) for 24 hr. Whole protein lysates were used to analyze the levels of AR signaling proteins by Western blot and GAPDH was used as the loading control. (D) MDA-MB-453 cells were pretreated with charcoal-stripped serum (CSS) contained medium for 72 h. Cells were then treated with 1 nM AR agonist R1881 alone or in combination with different concentrations of ARD-61 for 24 h. Expression of AR targeted genes were analyzed by qPCR and normalized to GAPDH. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3).