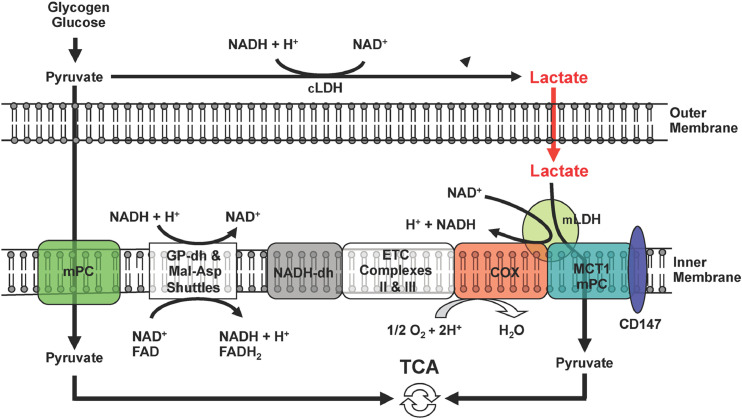
Fig. 6.
A schematic showing the putative mitochondrial lactate oxidation complex (mLOC). The lactate-pyruvate transporter (MCT1) is inserted into the mitochondrial inner membrane, strongly interacting with its chaperone protein CD147, and is also associated with cytochrome oxidase (COx) as well as mitochondrial lactate dehydrogenase (mLDH), which could be located at the outer side of the inner membrane. Lactate, which is always produced in the cytosol of muscle and other tissues because of the abundance, activity, and characteristics of cytosolic LDH, is oxidized to pyruvate via the lactate oxidation complex in mitochondria of the same cell. This endergonic lactate oxidation reaction is coupled to the exergonic redox change in COx during mitochondrial electron transport. ETC = electron transport chain; GP = glycerol phosphate; Mal-Asp = malate-aspartate; MCT = monocarboxylate (lactate) transporter; mPC = mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; TCA = tricarboxylic acid. Redrawn from Ref. 75 with permission.