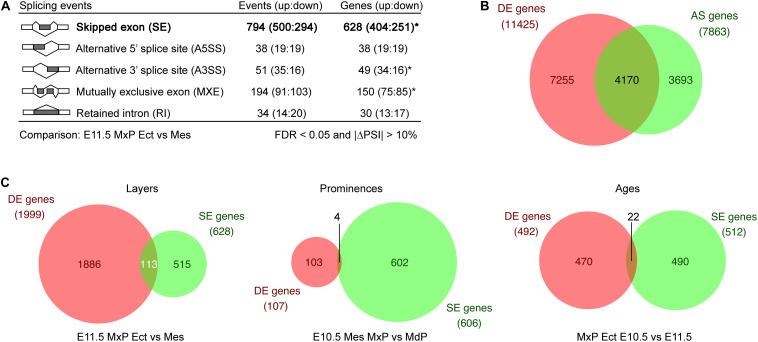
FIGURE 2.
Alternative splicing program during facial development. (A) Alternative splicing events called by rMATS by categories from comparison between E11.5 MxP ectoderm and mesenchyme with cutoffs as FDR < 0.05, |ΔPSI| > 10%, and at least one sample with five inclusion read counts or skipping read counts. For the diagrams of the five types of alternative splicing events, dark gray rectangles are the alternative used exons or the retained intron, while white rectangles are the conserved exons. Lines indicate splicing. Asterisks indicate that some of the genes have both up events or down events. (B) Many genes are regulated only by differential alternative splicing during facial development. Venn diagram showing the comparison between differentially expressed (DE) genes and differentially used alternatively spliced (AS) genes during facial development across all tissues. (C) Venn diagrams of individual layer, prominence, or age comparisons demonstrate there are few overlaps between DE and SE genes. AS, alternative splicing; DE, differentially expressed; Ect, ectoderm; Mes, mesenchyme; MdP, mandibular prominence; MxP, maxillary prominence.