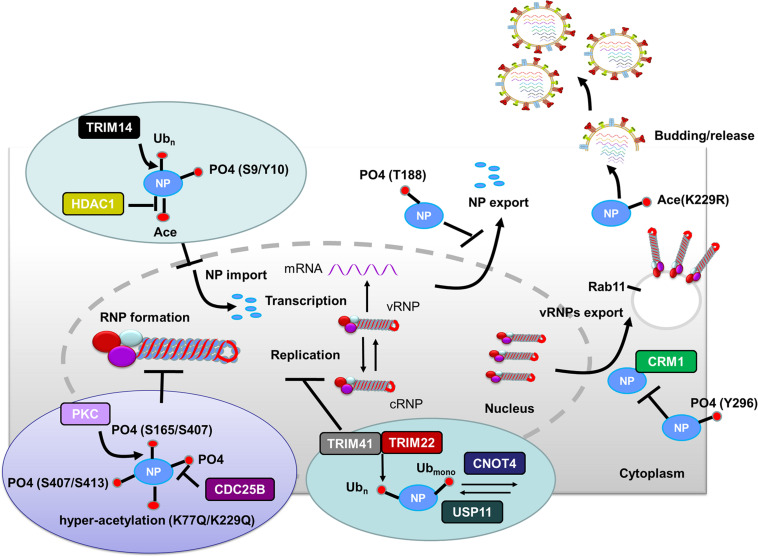
FIGURE 2.
Role of PTMs in regulating NP functions. Phosphorylation of NP at S9 and Y10 and ubiquitination of NP by TRIM14 prevent NP nuclear import. HDAC decreases NP acetylation and facilitates NP nuclear import. Phosphorylation of NP at S407 and S413 inhibits the assembly of influenza virus replication machinery. Mimicking hyperacetylation of NP at K77Q and K229Q disturbs vRNPs formation. Human PKCα blocks NP oligomerization through phosphorylating NP at S165 and S407. In contrast, CDC25B facilitates the dephosphorylation of NP, leading to enhanced NP self-oligomerization. TRIM41 and TRIM22 impede viral replication through ubiquitinating NP. The cellular deubiquitinating enzyme USP11 inhibits vRNA replication through deubiquitinating NP K184; CNOT4 competes with USP11 in the regulation of NP ubiquitination and enhances vRNA replication. Phosphorylation of NP Y296 impedes vRNPs nuclear export via inhibiting the interaction of NP with the export factor CRM1. Phosphorylation of NP T188 impedes NP nuclear export. Exported vRNPs associate with Rab11-positive vesicles and traffic from the cytoplasm to the apical cell surface for virion budding. NP acetylation plays a role in virion release. Abbreviations: Ub, ubiquitin and ubiquitination; PO4, phosphorylation; Ace, acetylation; vRNP(s), viral ribonucleoprotein(s); mRNA, messenger RNA; PKCα, protein kinase C α; CDC, cell division cycle; TRIM, tripartite motif; HDAC, histone deacetylase; USP11, ubiquitin–proteasome system protein 11; CNOT4, Ccr4-Not transcription complex subunit 4; CRM1, chromosome region maintenance 1 protein homolog.