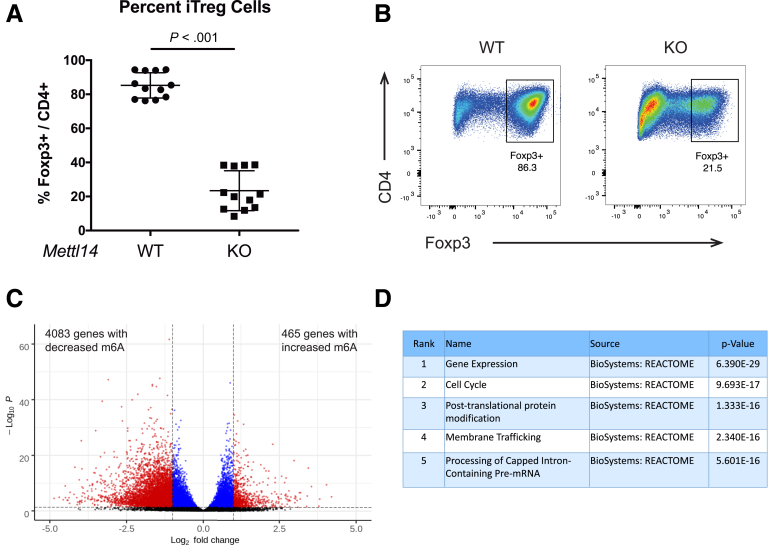
Figure 6.
Mettl14 deficiency causes impaired induction of naïve T cells into iTreg cells. (A) Induction efficiency of iTreg cells from naïve T cells as evidenced by Foxp3 expression. (B) Representative flow cytometry image showing percent of Foxp3+ iTreg cells after induction from naïve T cells. The cells were gated from a parent population of CD4+ cells. WT indicates wild-type littermate control. KO indicates CD4-Cre+/TgMettl14FL/FL conditional knockout. Data are represented as mean ± SD; n = 12 per group. Combined data from 3 independent experiments shown. (C) m6A profiling of iTreg cells compared with naïve T cells. Black color indicates nonsignificant; blue color indicates P < .05 and absolute Log2 fold change <1; red color indicates P < .05 and absolute Log2 fold change >1. (D) Significant pathways represented by genes with differential m6A levels. The top 5 most significant pathways were shown.