Fig. 7. Dual detection of SARS-CoV-2 by SENSR.
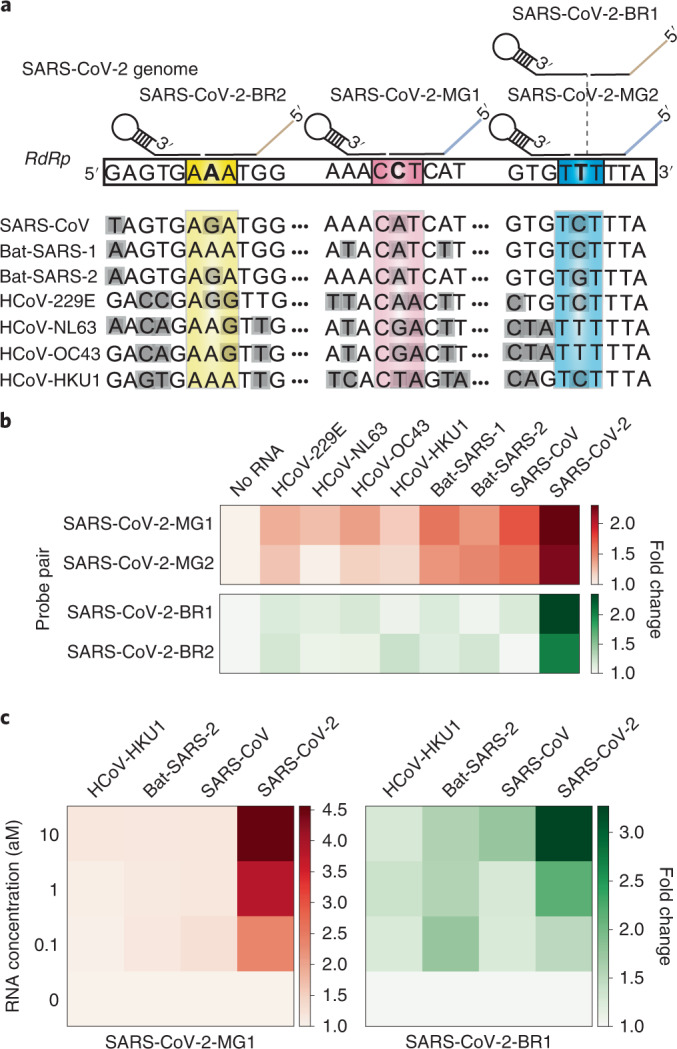
a, Probe design for dual-SENSR detection. Three regions in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) gene of SARS-CoV-2 were targeted. Discriminatory bases that enable the specific detection of SARS-CoV-2 against viruses with highly similar sequences are marked by bold letters. Grey shading indicates mismatches between the sequences of SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses. Only several bases around the ligation junction are displayed here. Entire probe-binding sites on the SARS-CoV-2 genome and sequence alignments are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8. b, Singleplex detection of 1 aM SARS-CoV-2 RNA by SENSR. c, One-pot dual detection of SARS-CoV-2 by the orthogonal probe pairs SARS-CoV-2-MG1 and SARS-CoV-2-BR1. All tests were performed with two biological replicates. Fold changes were calculated by dividing the normalized fluorescence values by the value with no target RNA. Bat-SARS-1, bat SARS-related coronavirus 1 (accession code: MG772933); Bat-SARS-2, bat SARS-related coronavirus 2 (accession code: NC_014470); HCoV-229E, human coronavirus 229E; HCoV-HKU1, human coronavirus HKU1; HCoV-NL63, human coronavirus NL63; HCoV-OC43, human coronavirus OC43.
