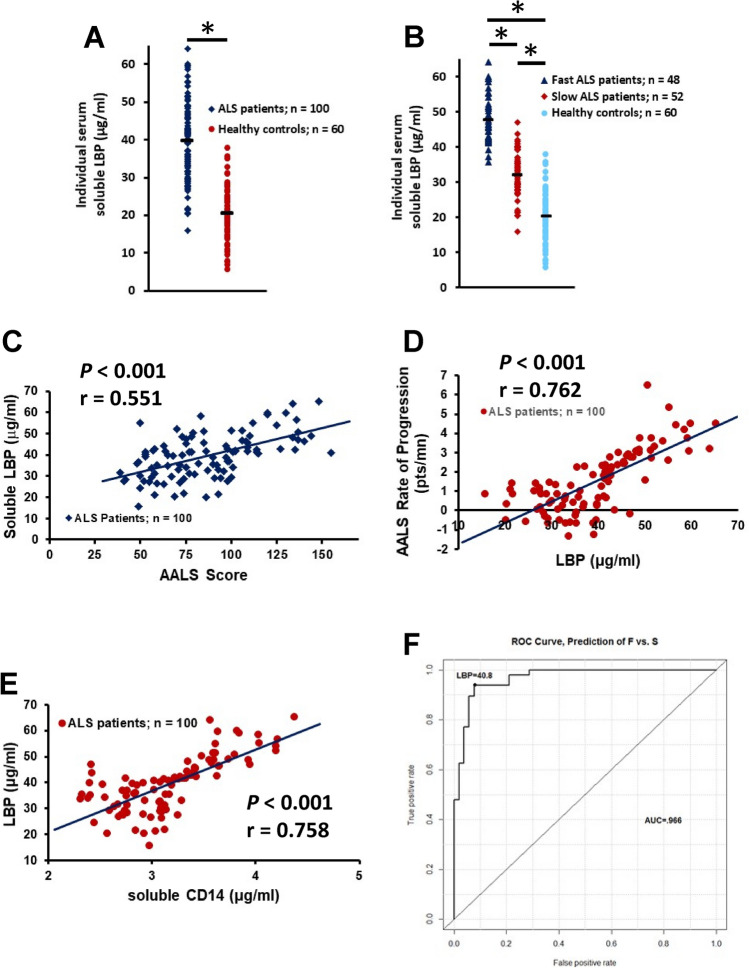
Figure 4.
Serum LBP is increased in patients with ALS and correlates with disease burden and disease progression rate. (A) LBP was increased in the serum of all patients compared with HC (*p < 0.001). (B) LBP was elevated in fast (*p < 0.001) and slowly (*p < 0.001) progressing patients compared with HC. LBP was elevated in the fast progressing patients compared with slowly progressing patients (p < 0.001). (C) Serum LBP positively correlated with the patient’s burden of disease. (D) Serum LBP positively correlated with the patient’s disease progression rate. (E) There was a positive correlation between LBP and sCD14. (F) Serum LBP levels were an accurate indicator of disease progression rates.