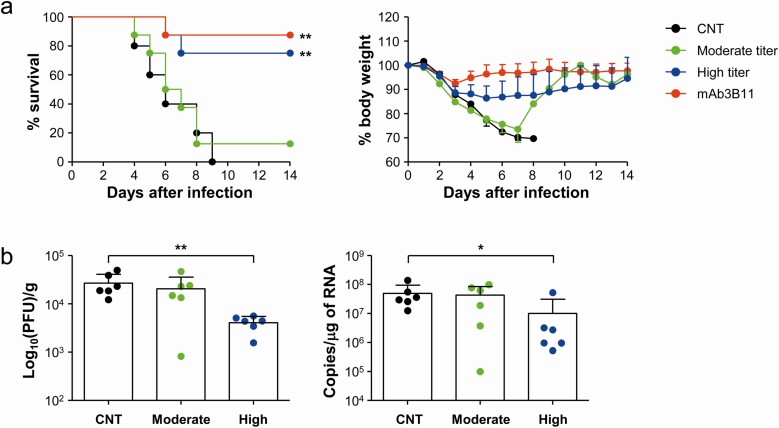
Figure 5.
Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of pooled sera from recovered patients in hDPP4-Tg mice. A, hDPP4-Tg mice were challenged intranasally with MERS-CoV at 2500 PFU/mouse (5 × LD50) and then treated with pooled sera (100 µL/mouse) or therapeutic mAb/3B11 (20 µg in 100 µL of PBS/mouse) four times (1 hour and 1, 2, and 3 days postinfection). The antibody titers and neutralizing activity (PRNT50) of pooled sera (negative, moderate, and high titer) are summarized in Table 2. Virus-challenged mice were monitored for 14 days to evaluate survival rate (left) and body weight changes (right). The body weight data are presented as means + SD of mice in each group (CNT: n = 5, moderate, high titer, and mAb/3B11: n = 8). Significant differences between the experimental group and control group (CNT) treated with non-immune sera are indicated (**, P < .01). B, MERS-CoV viral loads were assessed by measuring PFU (left) and copy numbers of viral RNA (right) in lung tissues collected at 4days after infection. Statistical significance between the experiment group and control group was tested by using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. Abbreviation: MERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. *, P < .05; **, P < .01.