Figure 4.
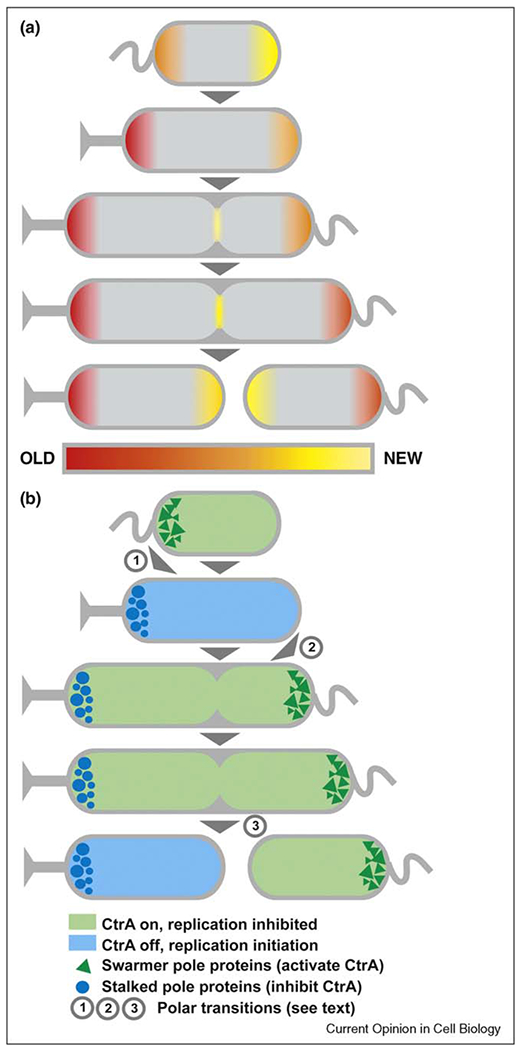
Polar maturation in Caulobacter crescentus. (a) Cell poles ‘age’ over the course of cell division. (b) In C. crescentus, polar aging is coupled with the timing of chromosome replication, transitions in polar protein composition, and cell cycle progression. Important polar transition periods are numbered (1: regulatory proteins are switched at swarmer to stalked pole transition; 2: assembly of cell cycle regulators at new pole; 3: compartmentalization and formation of new poles at cell division). Different sets of polar regulatory proteins promote (blue shading) or inhibit (green shading) chromosome replication by controlling the activity of a master regulator, CtrA.
