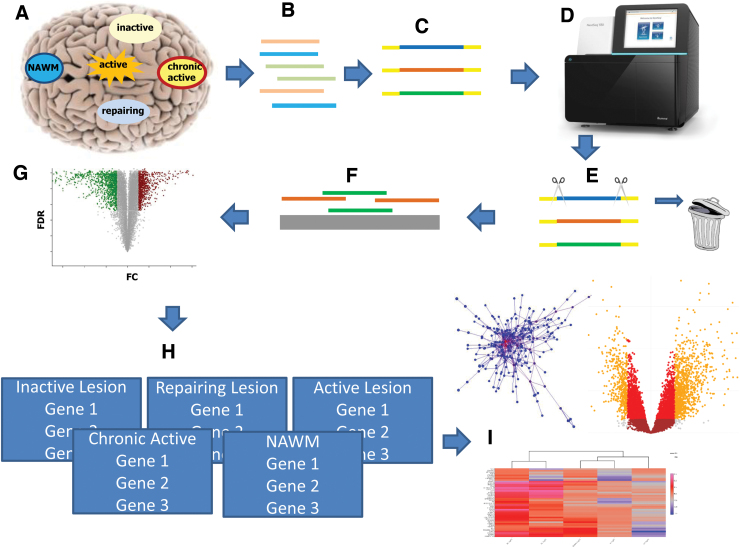
FIG. 1.
Graphical summary of the study. (A) With immunohistochemistry, we classified different lesion types (NAWM, active, inactive, chronic active, and remyelinating), and microdissected 98 of these brain areas from 10 progressive MS and 5 non-neurological disease brains. (B) Total RNA (microRNA, lncRNA, and protein coding) was extracted and (C) library was generated. (D) The templates were sequenced on a NextSeq550 using paired end, followed by (E) quality control, where all reads <Q20 were removed. (F) Remaining reads were aligned to the human genome and counted. (G) Statistical calculations were performed in R and the significant threshold was set to FDR <0.05. (H) MS Atlas was implemented based on RShiny offering three major visualizations (I): heatmaps, mechanistic candidate networks, and volcano plots. FDR, false discovery rate; logFC, log2-fold-changes; MS, multiple sclerosis; NAWM, normal appearing white matter.