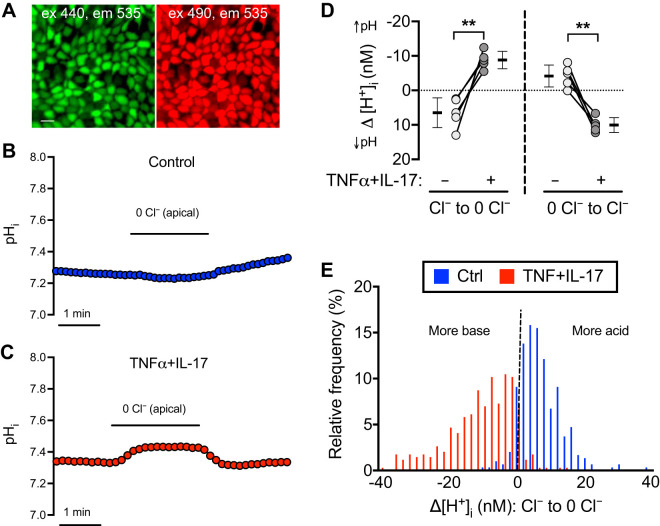
Fig. 7.
TNFα+IL-17 induce apical membrane Cl−/ exchange. Human airway epithelia were treated with either vehicle or TNFα+IL-17 for 48 h. Epithelia were washed, loaded with BCECF, and fluorescence measured with a confocal microscope. A: BCECF-loaded airway epithelia viewed en face. Scale bar, 10 μm. B and C: intracellular pH (pHi) responses to varying apical buffer composition in control (blue) and TNFα+IL-17-treated (red) epithelia. D: pHi values were converted to [H+]i and used to calculate net flux (Δ[H+]i) in response to removal (left) and replenishment (right) of Cl− in the apical perfusion buffer (n = 5 different donors). Bars indicate means ± SD. Groups were compared with paired Student’s t test. **P < 0.01. E: Δ[H+]i in response to Cl− removal from apical perfusion buffer was calculated at single-cell level by drawing regions of interest around single cells in BCECF-loaded epithelia. Results from 297 cells from control epithelia and 347 cells from TNFα+IL-17-treated epithelia were plotted as frequency distribution. Both distributions were nonnormal by Anderson–Darling test for normality (P < 0.0001).