Figure 5.
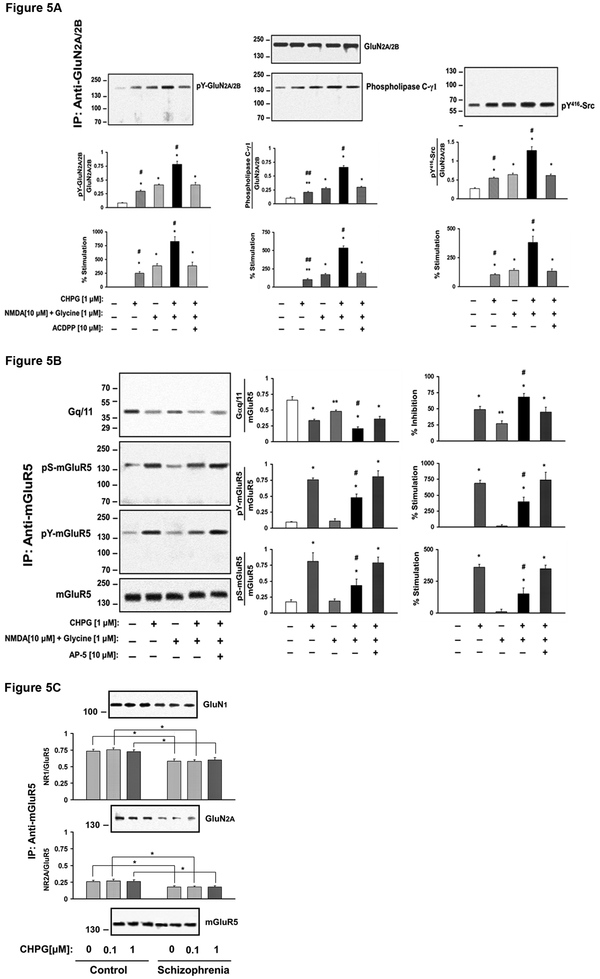
Fig 5A. GluN activation increases mGluR5 signaling in the DLPFC. DLPFC slices from 3 control subjects were examined for the effects of GluN activation on mGluR5-Gq/11 coupling. Prefrontal cortical slices were incubated 1 µM CHPG, NMDA (10 µM) + glycine (1 µM) or combination of CHPG, NMDA+glycine for 15 min in the presence or absence of 10 µM of ACDPP, a mGluR5 antagonist. The results indicate GluN activation leads to dephosphorylation of mGluR5 and enhance mGluR5 coupling to Gq/11. N = 3. Fig 5B. mGluR5 activation enhances GluN activation. DLPFC slices were incubated with 1 µM CHPG, NMDA (10 µM) + glycine (1 µM) or combination of CHPG, NMDA+glycine in the presence of absence of 10 µM of AP-5, a GluN antagonist. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-GluN2A and –GluN2B and pS416Src, phospholipase Cγ1 was probed by immunoblotting. N = 3. Fig 5C. mGluR5 association with GluN is markedly reduced in postmortem DLPFC from schizophrenia subjects. DLPFC slices were incubated with 0, 0.1 or 1 µM of CHPG for 15 min, and tissue lysates were IPed for mGluR5 complexes. IPs were probed for GluN1 and GluN2A by immunoblotting. mGluR5 –GluN association is reduced in schizophrenia. N = 17.