Fig. 1. Colloidal giant-shell CdSe/CdS quantum dots and experimental setup.
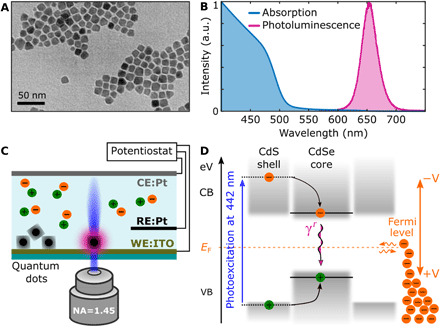
(A) TEM image of batch 2. (B) Absorption and photoluminescence spectra of batch 2. a.u., arbitrary units. (C) Sketch of a confocal microscope focused on an individual quantum dot subjected to a voltage bias between reference (RE) and working (WE) electrodes of a three-electrode electrochemical cell, while a Pt-coiled wire served as a counter electrode (CE). NA, numerical aperture. (D) Energy diagram of a quantum dot with valence (VB) and conduction (CB) bands accommodating an exciton. A 442-nm laser induces above bandgap excitation of the carriers in the CdS shell, which can relax to the CdSe core recombining radiatively at γr = γ0 rate. The position of the Fermi level (orange dashed line) can be manipulated via the application of a voltage bias and adjusted for the electron injection into the conduction band, leading to exciton charging.
