Fig. 1.
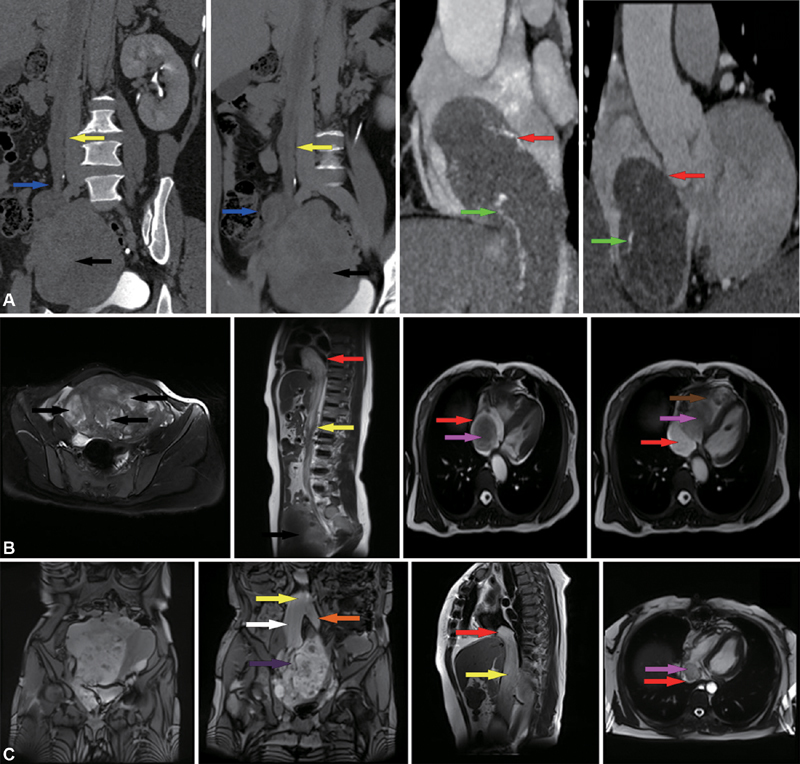
( A ) A CT (computed tomography) scan from case A is shown. The volume of the uterus is significantly enlarged and complicated with multiple uterine fibroids. Multiple masses are extending into the right ovarian vein and the inferior vena cava (IVC) and right atrium (RA). An enhanced vascular shadow can be seen in the lesion ( green arrow ). ( B ) A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) from case B shows multiple uterine fibroids. The tumor extends from the IVC to the RA. The tumor could be observed moving with the movement of the RA. The distal portion of the tumor traverses the tricuspid valve into the RV during diastole. ( C ) The MRI from case C indicates a large, multilobulated, complex pelvic mass closely related to the uterus. The uterus deviates left due to pressure. The mass extends from the right internal iliac vein and the common iliac vein and extends into the IVC and RA ( red arrow ); RV (brown arrow); mass (pink arrow); IVC (yellow arrow); Right ovarian vein (blue arrow); Right common iliac vein (white arrow); Left common iliac vein (orange arrow); Right internal iliac vein (purple arrow); Uterine fibroids (black arrow).
