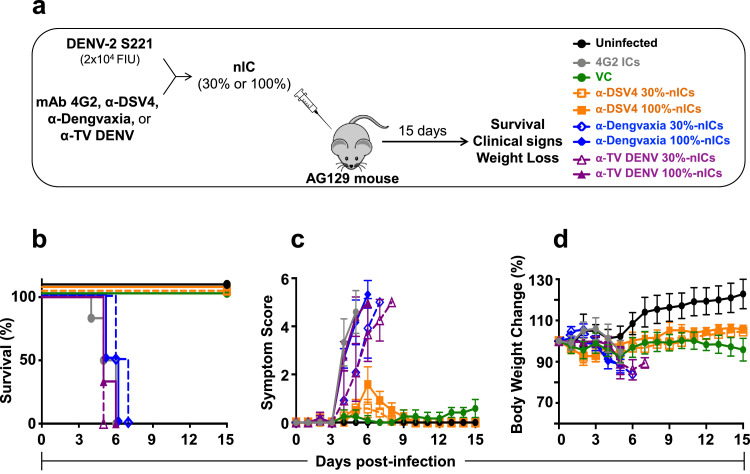
Fig. 3.
Evaluation of in vivo ADE capacity of BALB/c immune sera by inoculation of nICs into AG129 mice. Groups of AG129 mice (n=6) were given intravenous (retro-orbital) injections of nICs, generated by pre-incubating 20,000 FIUs of DENV-2 S221 with α-DSV4 antiserum, α-Dengvaxia antiserum or α-TV DENV antiserum, on day 0 (panel ‘a’). The amounts of antisera used were such that the virus in the nIC was either fully (100%, using ~5 µl immune serum) or partially (30%, using 0.08–0.32 µl immune serum) neutralised (based on residual infectivity measured using the Vero cell-based FACS assay). In parallel, control groups of mice which received no treatment (Uninfected), only the virus in the absence of any antiserum (virus control, VC) or nICs (containing 100% neutralised virus) generated using the FLE-specific CR mAb 4G2 (10 µg), were also included. The mice were monitored for survival (panel ‘b’, Kaplan-Meir survival analysis), clinical symptoms (panel ‘c’) and body weight change (panel d’), for up to 15 days post nIC inoculation. In panels ‘b–d’, the data for the different groups are indicated as follows: the Uninfected (black curves), VC (green curves) and mAb4G2-IC (grey curves) groups are shown by solid curves in different colours as indicated. For groups receiving nICs made using α-DSV4 (orange curves), α-Dengvaxia (blue curves) or α-TV DENV (purple curves) antisera, those receiving the 100% and 30% neutralised ICs, are indicated by solid and dashed curves, respectively. Survival data (panel ‘b’) were analysed by Log-Rank (Mantel-Cox) test for significant difference in survival rates. Survival of mice in α-DSV4 30% and 100% nIC groups was not significantly different from that of uninfected mice. In comparison, survival of mice in all the other experimental groups was significantly compromised (p≤0.001). Clinical scoring in panel ‘c’ and body weight measurements in panel ‘d’, were as described in Fig. 2 legend (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).