Figure 4. Developing plasmid-free 1-octanol producing strain.
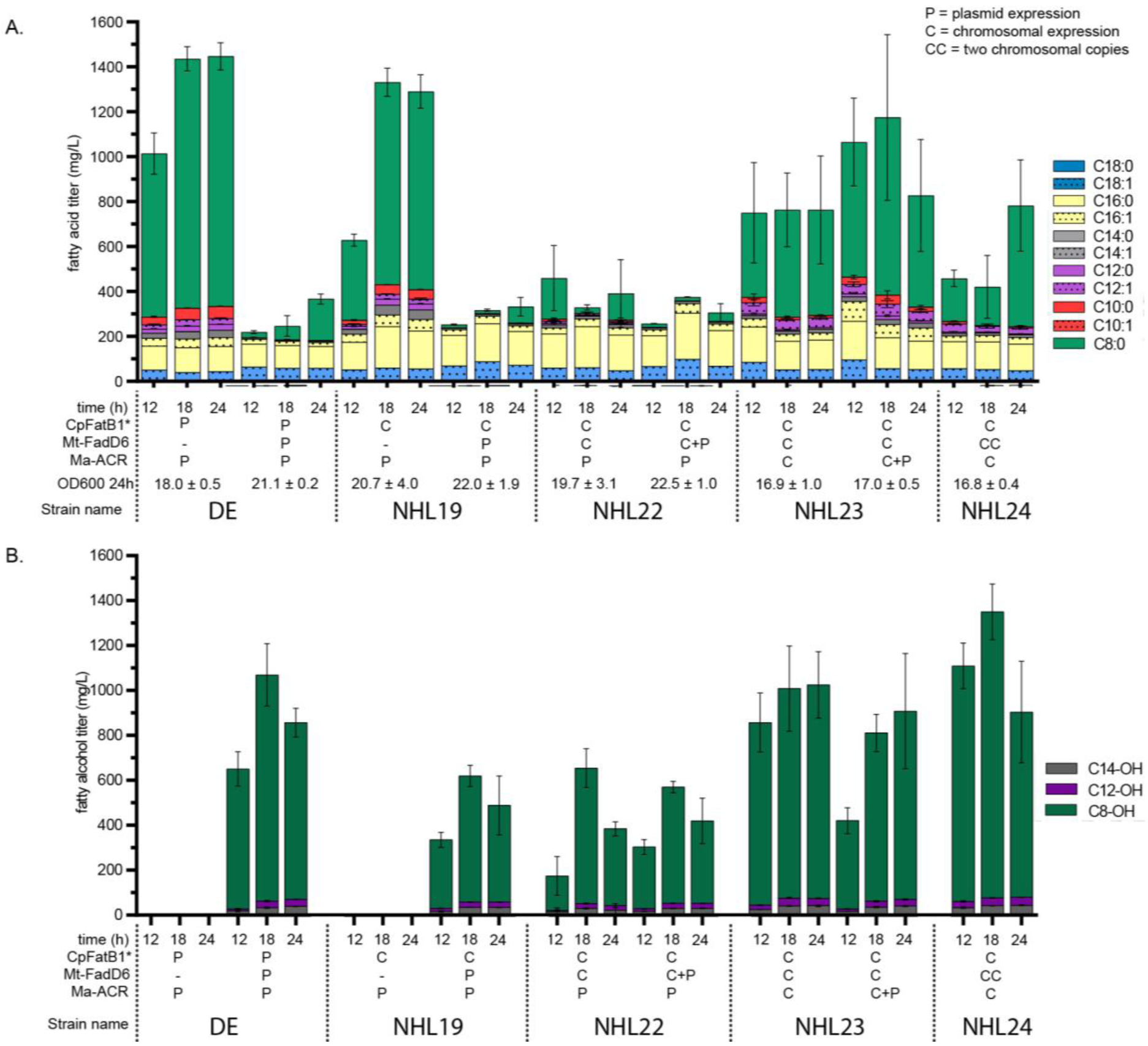
Strains containing 1-octanol pathway enzymes are first expressed exclusively from plasmids (strain DE, first panel) and then the genes were added systematically into the chromosome (strains NHL19 and NHL22; second and third panels, respectively) until reaching fully chromosomally expressed strain (NHL23, fourth panel). Finally, a second copy of Mt-FadD6 was added to the chromosome (NHL24, fifth panel) (A) indicates the fatty acid, and (B) fatty alcohol titer for strains DE (ΔfadD ΔfadE) (first panel); NHL19 (ΔfadE ΔfadD::PTRCCpFatB1*) (second panel); NHL22 (ΔfadE ΔfadD::PTRCCpFatB1* ΔackA-pta::PTRC-MtFadD6) (third panel); NHL23 (ΔfadD::PTRCCpFatB1* ΔfadE ΔackA-pta::PTRC-MtFadD6 ΔFadBA::PTRCMaACR) (fourth panel); and NHL24 (ΔfadD::PTRCCpFatB1* ΔfadE ΔackA-pta::PTRC-MtFadD6 ΔpoxB::PTRC-MtFadD6 ΔFadBA::PTRCMaACR) (fifth panel). Chromosomally expressed genes are indicated by a ‘C’ and plasmid expressed are denoted by a ‘P’. Genes being expressed both chromosomally and in plasmid are denoted as ‘C+P’. OD600 for 24 h time points are shown as well.
