Figure 8). Ad5 targets Cx43 in cardiomyocytes and induces Cx43-gap junction remodeling.
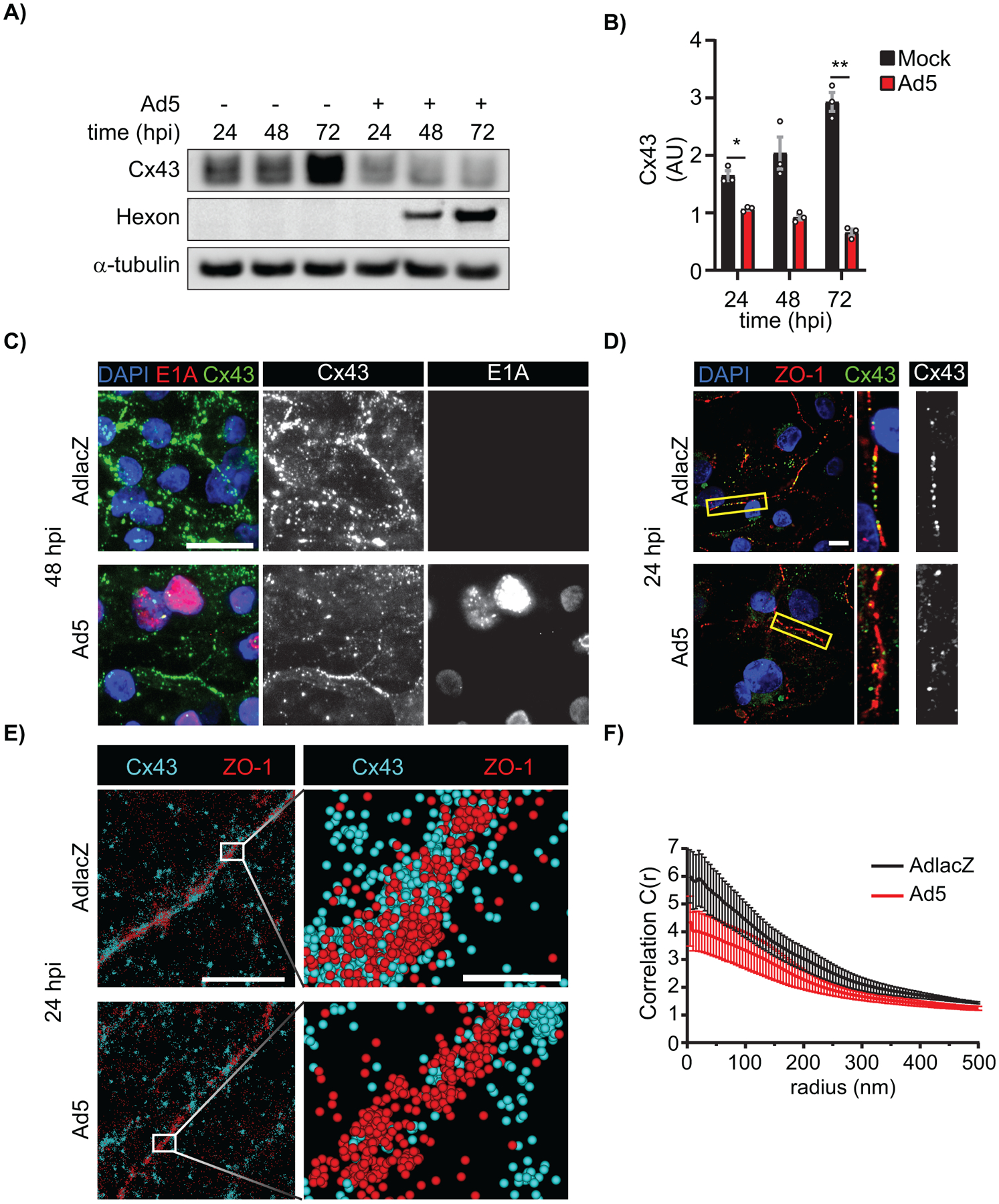
HiPSC-CMs were infected with Ad5 or replication-incompetent AdlacZ at a MOI of 10 iu/cell and protein harvested or fixed for immunolabeling over a 72 h time course. A) Western blot probed for Cx43 expression in HiPSC-CMs. Detection of Ad5-Hexon protein expression serves to confirm infection and α-tubulin serves as loading control. B) Densitometry analysis of A. C) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of HiPSC-CMs at 48 hpi probed for Cx43 (green) and adenovirus E1A (red) with nuclei identified using DAPI (blue). Original magnification: X100. Scale bar: 20μm. D) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of HiPSC-CMs 24 hpi probed for Cx43 (green) and ZO-1 (red) with nuclei identified using DAPI (blue). Original magnification: X100. Scale bar: 10μm. Images representative of 3 separate experiments. E) Super resolution stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) derived point-cloud localizations of Cx43 (cyan) and ZO-1 (red) in Ad5- and AdlacZ-infected HiPSC-CMs 24 hpi. Zoomed out panels (left) scale bar: 2μm. Zoomed in panels (right) scale bar: 200nm. Sphere size: 30nm. F) Cross-Pair correlation functions for Cx43/ZO-1 complexing in E. (n=10). Statistical analysis was performed with two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (B) (n=3). *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p<0.0001. Data are represented as mean ±SEM.
