Figure 4. Elevated TRIM37 leads to a reduction in CEP192 that confers enhanced sensitivity to PLK4 inhibition.
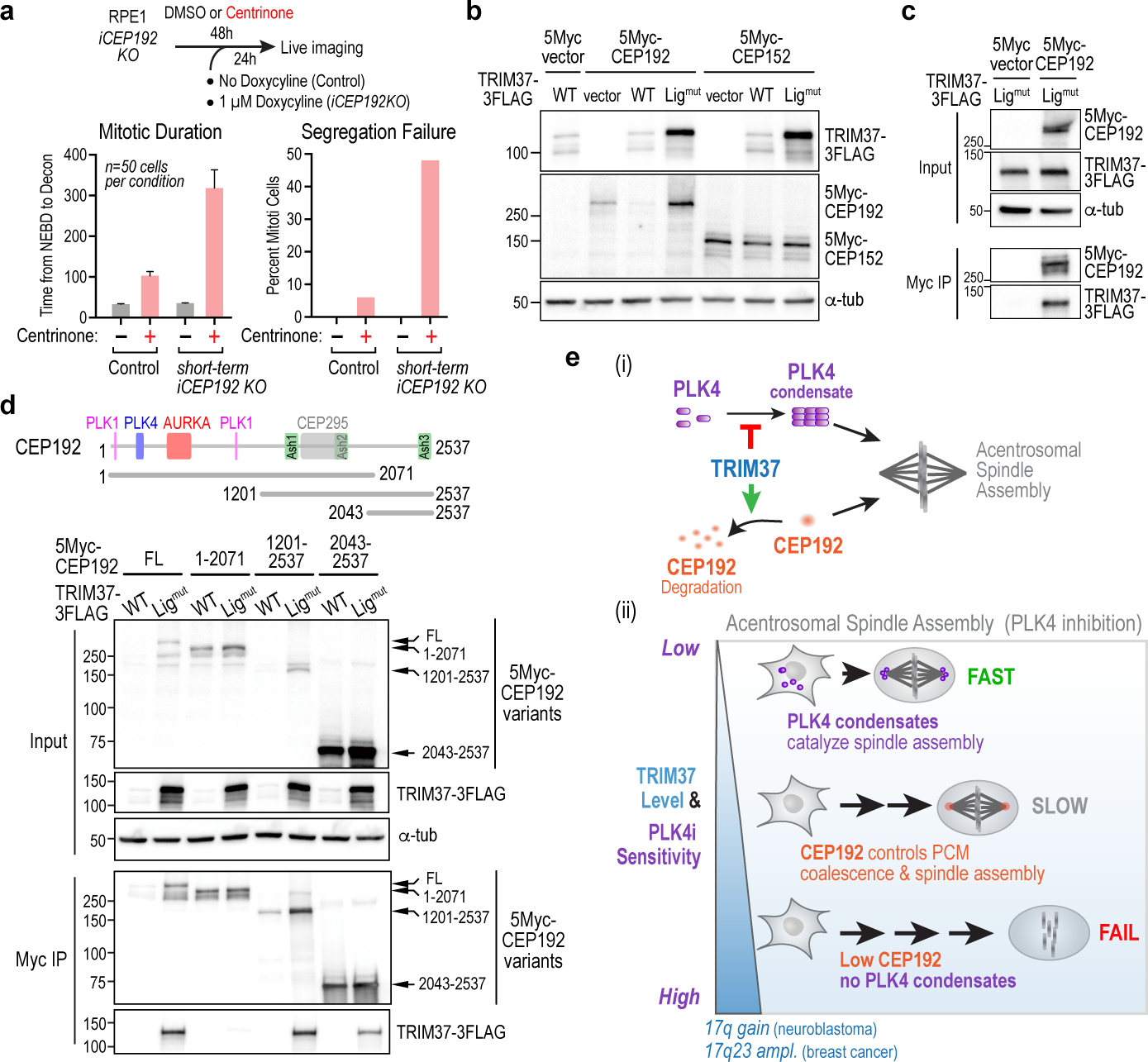
(a) (top) Approach for partial CEP192 inhibition using a short-term inducible knockout. (bottom) Graphs plot mitotic duration and percent segregation failure. Short-term inducible CEP192 knockout does not affect mitosis in DMSO-treated cells but significantly enhances mitotic defects in centrinone-treated cells. (b) Co-expression with WT or ligase-inactive TRIM37 shows that CEP192, but not CEP152, protein levels are controlled by TRIM37 ligase activity. α-tubulin serves as a loading control. (c) Interaction analysis showing that co-expressed ligase-inactive TRIM37 associates with CEP192. α-tubulin serves as an input loading control. (d) Schematic highlights key interaction sites in CEP192. Input blot shows effects of co-expressed TRIM37 (wildtype or ligase-inactive) on stability of CEP192 fragments; immunoprecipitation blot assesses association with ligase-mutant TRIM37. α-tubulin serves as an input loading control. Note that when CEP192 is unable to interact with TRIM37 due to deletion of its C- terminus (1–2071), levels are not affected by TRIM37 WT co-expression. (e) Model depicting how TRIM37 exerts bi-directional control over acentrosomal mitosis following PLK4 inhibition. (i) Two ligase activity-dependent functions of TRIM37 are to prevent PLK4 self-assembly into condensates that nucleate microtubules and to target CEP192 for degradation. (ii) When TRIM37 levels are low, PLK4 forms condensates that catalyze robust acentrosomal spindle assembly. When TRIM37 levels are normal, TRIM37 prevents PLK4 from forming condensates; after mitotic entry, foci containing pericentriolar material components coalesce concomitant with slow acentrosomal spindle assembly. When TRIM37 levels are high, CEP192 levels are reduced and there are no PLK4 condensates—consequently, acentrosomal spindle assembly fails. Amplification of the genomic region containing TRIM37 in neuroblastoma and a subset of breast cancers highlights the potential for synthetic lethality with PLK4 inhibition in specific cancer contexts. For gel source data see Supplementary Figure 1.
