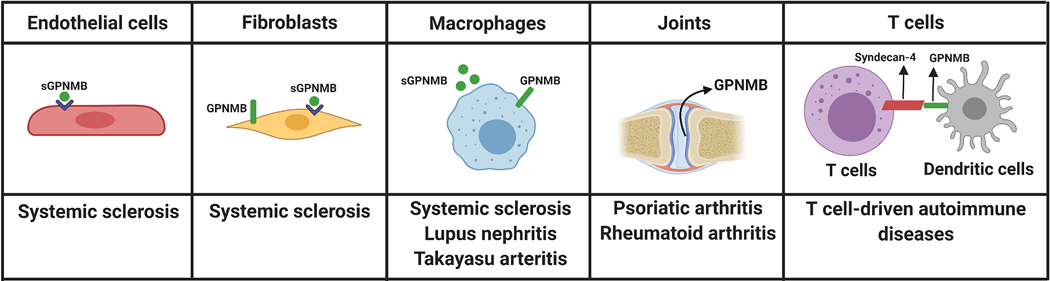
Figure 4. Schematic representation demonstrating potential involvement for GPNMB in multiple autoimmune diseases.
Dysregulation of GPNMB, particularly the soluble form, could play a role in systemic sclerosis, as GPNMB mediates pro-angiogenic effects on endothelial cells, anti-fibrotic potential on fibroblasts, and anti-inflammatory properties in macrophages. GPNMB-expressing macrophages also play a role in lupus nephritis and Takayasu arteritis. The expression of GPNMB in the synovial tissue has been reported in both psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Since GPNMB on antigen presenting cells, such as dendritic cells, inhibits T-cell activation by binding to syndecan-4 on T cells, this interaction might be relevant to T cells-driven autoimmune diseases.