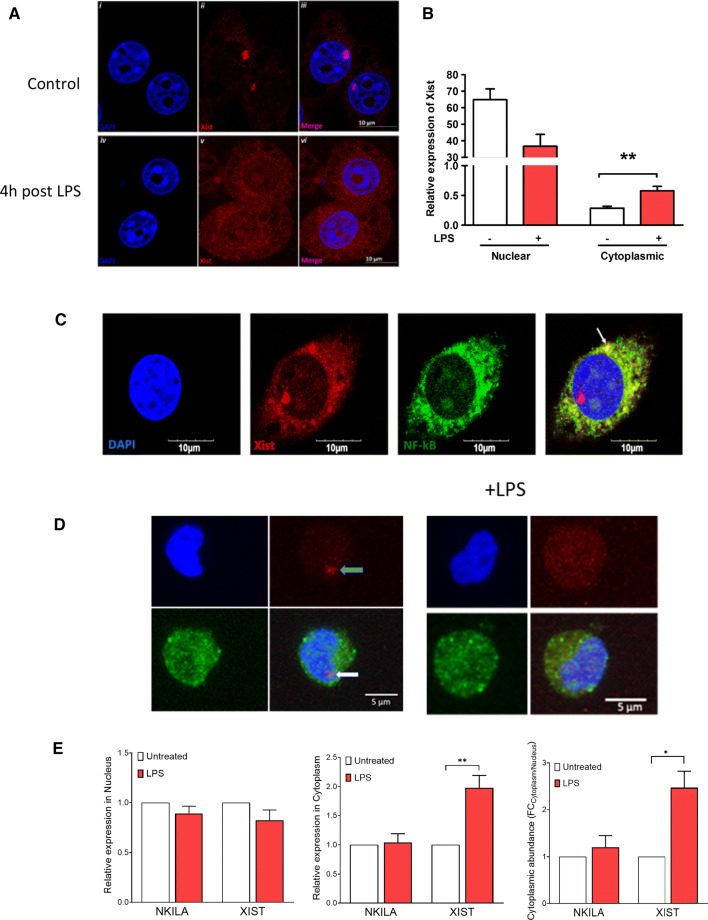
Fig. 3.
Xist translocates to the cytoplasm in response to LPS, and colocalizes with NF-κB. a Confocal images showing FISH for Xist in J774A.1 cells after LPS stimulation (1 µg/ml for 4 h); blue-DAPI, red-Xist. b Relative expression of Xist in nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments of J774A.1 cells in response to LPS stimulation (1 µg/ml for 4 h). c Confocal images showing FISH for Xist and immunostaining of p65 subunit of NF-κB in J774A.1 cells after LPS stimulation (1 µg/ml for 4 h); blue-DAPI, red-Xist, and green-NF-κB. Arrow points to co-localization of Xist and p65 subunit of NF-κB. d Confocal images showing FISH for XIST and immunostaining of p65 subunit of NF-κB in AML193 cells without (labeled control) and after LPS stimulation (1 µg/ml for 4 h); blue-DAPI, red-Xist, and green-NF-κB. e Relative expression of Xist in nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments of AML193 (human female monocytic cell line) in response to LPS stimulation (1 µg/ml for 4 h). NKILA, a cytosolic lncRNA that is known to interact with NF-kB was used as control