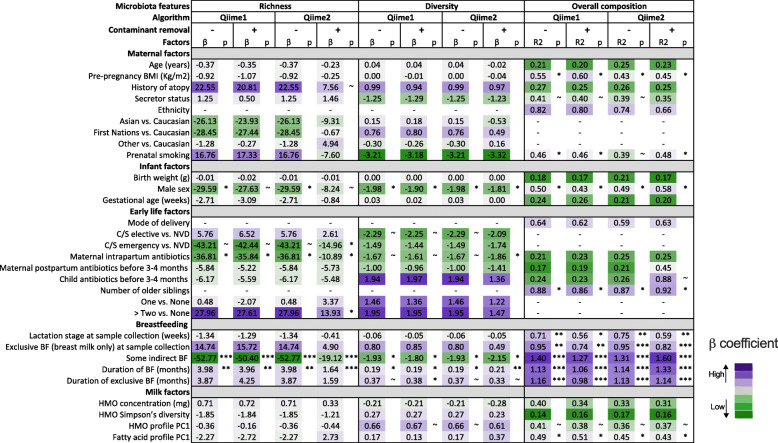
Fig. 3.
Impact of four sequence processing approaches on observed associations of milk microbiota richness (observed OTUs/ASVs), diversity (inverse Simpson index), and overall composition with maternal, infant, early life, breastfeeding, and milk factors. We re-processed our published 16S rRNA gene sequencing milk microbiota dataset [19] using Qiime1 and Qiime2 with or without contaminant removal resulting in four datasets (see also Fig. 1a). Beta coefficients from univariate linear regression (richness and diversity) or R2 from redundancy analysis (overall composition) are presented and colour coded within each microbiota feature. Results of Qiime2 with contaminant removal are originally reported in Moossavi et al. [19]. BF, breastfeeding; BMI, body mass index; C/S, Cesarean section; HMO, human milk oligosaccharide; NVD, normal vaginal delivery; PC1, Principal Component 1 * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001